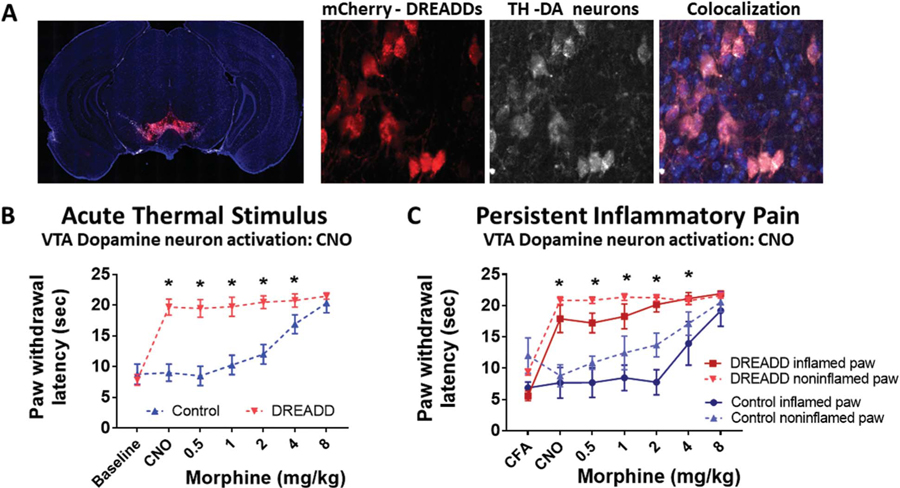
Figure 5.
Direct VTA dopamine neuron stimulation is antinociceptive, diminishing both acute thermal and CFA-induced inflammatory pain. (A) AAV-hsyn-DIO-hM3D(Gq)-mCherry expression in the VTA of a representative Dat-cre mouse. hM3D expression is visualized through the red mCherry tag. Immunohistochemical staining of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) indicating the cell bodies of dopaminergic neurons. The overlayed image showing colocalization of hM3D in TH-expressing neurons of the VTA. (B) Effect of intraperitoneal (i.p.) clozapine-N-oxide (CNO) and morphine on paw withdrawal latency to a thermal stimulus in DAT-cre mice expressing hM3D in the VTA (DREADD) or controls lacking the receptors (Control). Mean (±95% CI), *P < 0.001, 2-way ANOVA. (C) Effect of i.p. clozapine-N-oxide (CNO) and morphine on thermal paw withdrawal latency in mice with CFA-induced ankle joint inflammatory pain. Mean (±95% CI). *P < 0.05, t tests with the Holm–Sidak correction. CFA, complete Freund adjuvant; CI, confidence interval; VTA, ventral tegmental area.