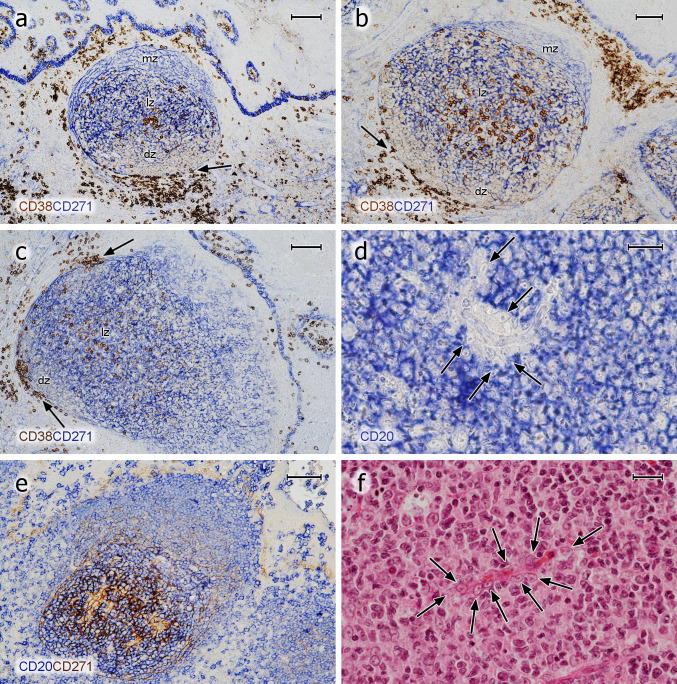
Fig. 2.
Distribution of CD38++ PCs and pericapillary FDCs in tonsil GCs. a–c Staining for CD38++ PCs (mAb SPC32, brown) followed by visualisation of CD271+ FDCs (mAb EP1039Y, blue). PCs may accumulate in the basal light zone and/or distribute evenly in the light zone and occur at the surface of the GC. They also form rows of cells at the dark zone surface, which are connected to PC clusters in the lamina propria outside the GC (arrows). The basal layer of the crypt epithelium is also CD271+. d FDCs at the surface of intra-GC microvessels (arrows) prevent CD20+ B lymphocytes (mAb L26, blue) from approaching the endothelium. e The unstained cells in d are CD271+, when CD20 is demonstrated in blue (mAb L26) followed by CD271 in brown (mAb EP1039Y). f The nuclei of the pericapillary FDCs (arrows) are also visible in routine HE-stained sections. mz mantle zone, lz light zone of GC, dz dark zone of GC. a, b 21-year-old female. c 12-year-old female. d, e 38-year-old female. f 57-year-old male. Scale bars 100 µm (a, c), 70 µm (b, e), 20 µm (d, f)