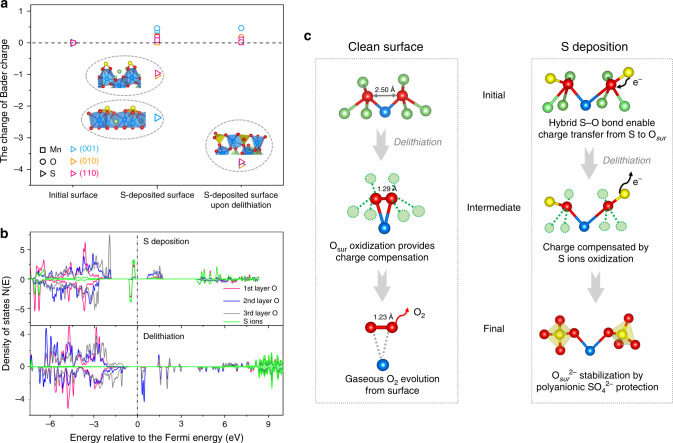
Fig. 4. Surface charge transfer of sulfur-deposited Li2MnO3 and the mechanism of surface O stabilization.
a The change in Bader charge of surface Mn, O, and S (per atom) on the three outermost surfaces during the process of S deposition and latter extraction of 37.5% Li. Bader charge of surface Mn, O (per atom) on the initial surface, and S atoms has been normalized to zero. b Calculated local density of states of the first layer O to the third layer O and S ions upon S deposition and 37.5% delithiation. Here the (010) surface was taken as characteristic of the three surfaces of Li2MnO3. c Schematic of how S deposition stabilizes surface O during delithiation in the first cycle (right), by contrast to O2 evolution from the clean surface (left). From top to bottom: the coordination environment of the surface O ions pairs in full lithiation; the intermediate local structure after 37.5% delithiation; the final stable configuration of surface O ions pairs after 37.5% delithiation.