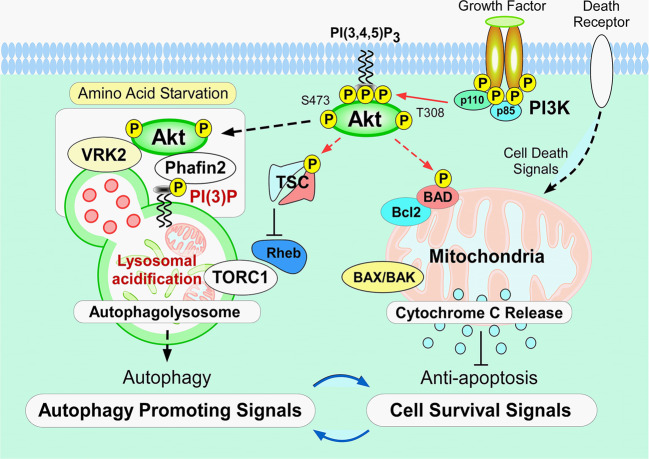
Fig. 2. Lysosomal Akt–Phafin2–VRK2 complex as a functional modulator of autophagy.
Regulatory roles of Akt at the lysosome in the course of autophagy are suggested by Beclin-1 (Atg6), transcription factor EB (TFEB), and Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 (ULK1) functioning as direct substrates23,54,55. Recent investigations revealed that target molecules of Akt, such as the tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), Beclin-1 (ATG6), ULK1, and BAD, are present in the lysosomes23,48–52. Lysosomes are intracellular organelles that participate in intracellular protein degradation through activating hydrolytic enzymes in the process of autophagy for amino acid recycling8–10. Autophagy, a cell survival mechanism during starvation conditions, participates in the regulation of cell death/survival machinery5–7. Searching for the binding partner of Akt at the lysosome using yeast two-hybrid screening and time-of-flight/mass spectrometry analyses, we identified the formation of a Akt–Phafin2–VRK2 protein complexes at the lysosome in a phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P)-dependent manner16,48. A functional study demonstrated the regulatory roles of the Phafin2–VRK2–Akt protein complex at the lysosome in the course of autophagy induction. These findings support the notion that the intersection between autophagic cell death and apoptosis may be at the mitochondria. The presence of the Akt–Phafin2–VRK2 at the lysosome sheds light on the roles of cell death and survival machinery in mammalian cells that may underlie various human diseases including cancer and autoimmune diseases.