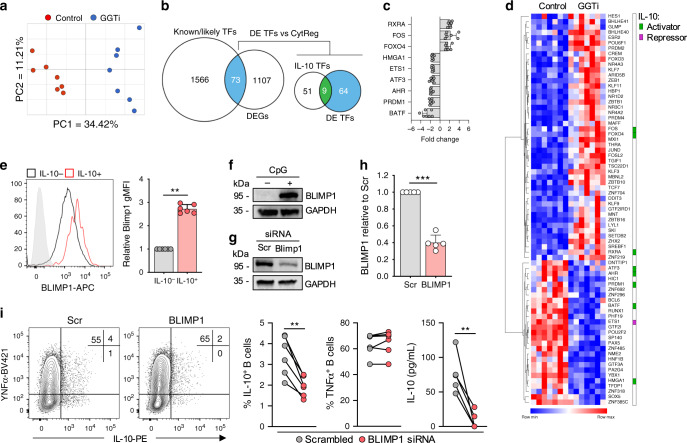
Fig. 5. GGPP regulates IL-10 induction via BLIMP1.
a Principal component analysis of human B cells after stimulation through TLR9 ± geranylgeranyl transferase inhibition (GGTi), with analysis performed on total normalized counts generated from RNA-sequencing data, before statistical analysis (n = 7). b Workflow for the identification of putative IL-10 transcription factors. First, differentially expressed genes were cross referenced with known or likely human transcription factors, and the subsequently identified differentially expressed transcription factors were cross referenced with previously validated IL-10 transcription factors in either macrophages or T cells. Differentially regulated IL-10 transcription factors are shown in (c) and all differentially regulated transcription factors are shown in (d) (n = 7). e Expression of BLIMP1 in human B cells within either IL-10+ or IL-10− B cells after stimulation through TLR9 (n = 6, pval = 0.003). f Western blot showing BLIMP1 expression in human B cells either in unstimulated or stimulated through TLR9 (CpG) after 40 h (representative of three independent experiments). g, h Western blot showing expression of BLIMP1 in human B cells after stimulation of TLR9 and nucleofection with either a scrambled control (Scr) or BLIMP1 siRNA (n = 5, pval = 0.001). i IL-10 and TNF expression in human B cells stimulated through TLR9 after nucleofection with either Scr or BLIMP1 siRNA (n = 6 for flow cytometry, pval = 0.002; and 5 for ELISA, pval = 0.009). Each data point represents individual donors. All data presented are mean ± SD where average values are shown. Statistical analysis in all figures was done using a paired t test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and all significant values are shown.