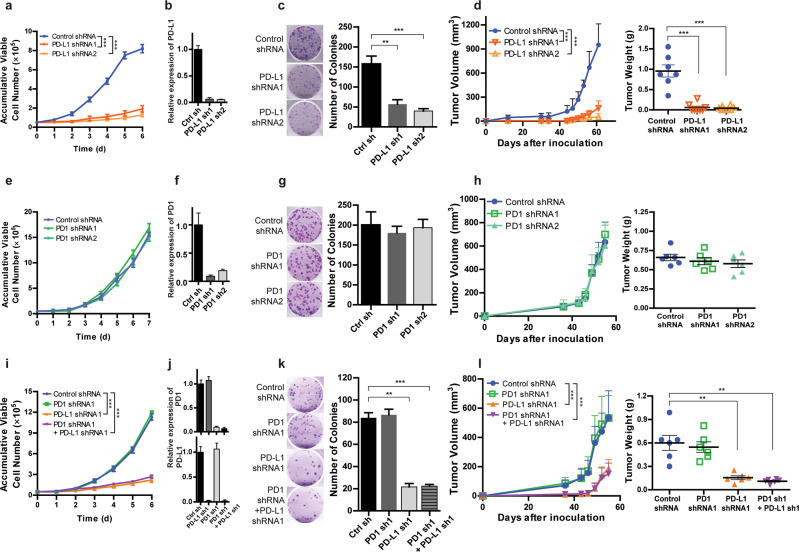
Fig. 1. PD-L1 is required for TNBC cell proliferation and tumor growth independent of PD1.
a–d PD-L1 promotes cell growth. MDA-MB-231 cells were infected with control shRNA or two different PD-L1 shRNA viruses. a Cell growth was monitored at indicated time points by cell counting. b PD-L1 knockdown efficiency was determined by qRT-PCR. c Colony formation assays were performed. d In vivo tumor growth in NSG mice was assessed and tumor weights were measured when experiments were terminated. e–h PD1 is dispensable for cell growth. e MDA-MB-231 cells expressing control shRNA or two different PD1 shRNAs were monitored for cell proliferation at indicated time points by cell counting. PD1 knockdown efficiency (f), colony formation (g), and tumor growth in NSG mice (h) were determined, respectively. i–l PD-L1-mediated cell proliferation is independent of PD1. i MDA-MB-231 cells expressing control shRNA, PD-L1 shRNA, PD1 shRNA, or a combination of PD-L1 shRNA and PD1 shRNA were monitored for cell growth. Knockdown efficiency (j) and colony formation (k) were independently replicated three times with similar results. l Tumor growth at different time points was determined and tumor weights were measured at the time when the experiments were terminated (n = 6–7). Data are presented as means ± SEM of n = 3 independent experiments. Student’s t-test was used for the comparisons for (c, d) (right panel), (g, h) (right panel), (k, l) (right panel), and 2-way ANOVA was used for (a, d) (left panel), (e, h) (left panel), (i, l) (left panel). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.