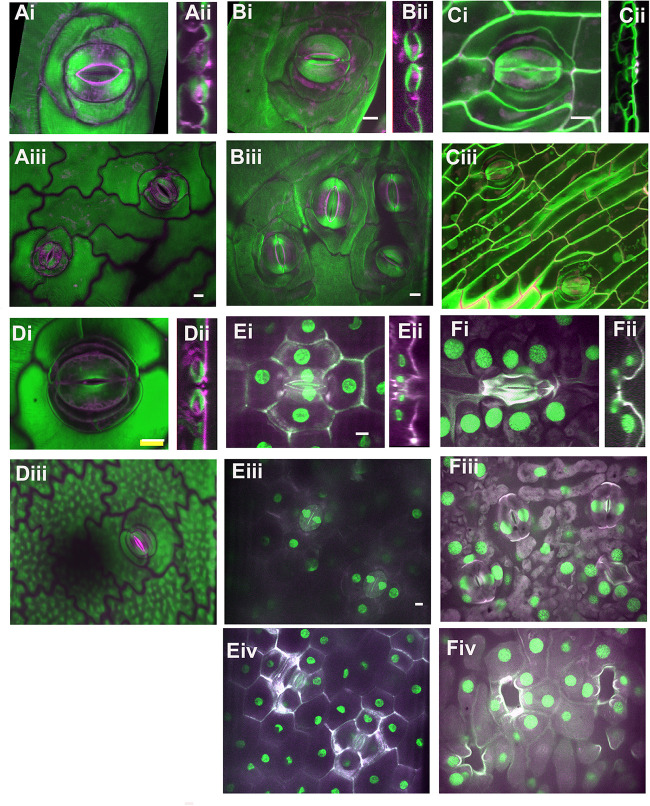
FIGURE 3.
Stomatal complex types, part 2. All images are imaged via confocal microscopy. Images (i,iii) are full or partial z-projections while image (ii) is a 3D-reconstructed side view through the stomatal pore. For sunken stomata in Agave and gingko (E,F) a lower focal plane containing the guard cells (iii) and a higher focal plane showing epidermal and subsidiary cells (iv) are shown. (A) Kalanchoe spp. (common unknown variety from garden center); anisocytic and heliocytic. (B) Begonia spp. (common unknown variety from garden center) – heliocytic (C) Didierea madagascariensis - unusual type (D) Anacampseros rufescens – tetracytic with four lateral subsidiary cells (E) Agave bracena – tetracytic with 2 lateral and 2 polar subsidiary cells. (F) Ginkgo biloba – cyclocytic. Green = Calcofluor White and Magenta = Direct Red, except for (E,F) where Green = Propidium Iodide and Magenta = Calcafluor White. All scale bars are 15 micrometers.