Figure 6.
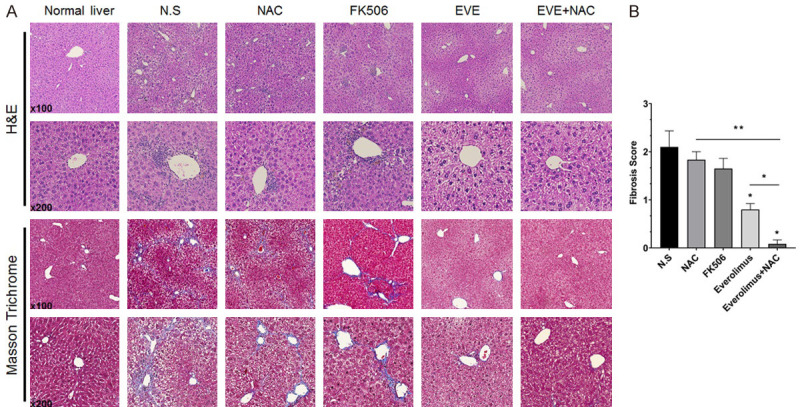
Effect of combination drugs on liver fibrogenesis and hepatic inflammation. A. Microscopy findings in rat liver sections. Progression of liver fibrosis is accompanied by inflammation and excessive extracellular matrix deposition. Everolimus, an mTOR inhibitor, prevented liver fibrosis induced by TAA and a high fat diet; liver morphology demonstrated by H&E staining. ECM production detected by Masson trichrome staining of mouse livers after 8 weeks of treatment, with co-administration of TAA and high-fat diet. Drug treatment, especially everolimus and its combination with NAC, suppressed collagen deposition in a fibrosis model. B. Fibrosis score evaluated by Masson trichrome-stained sections of mouse livers after 8 weeks. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001.
