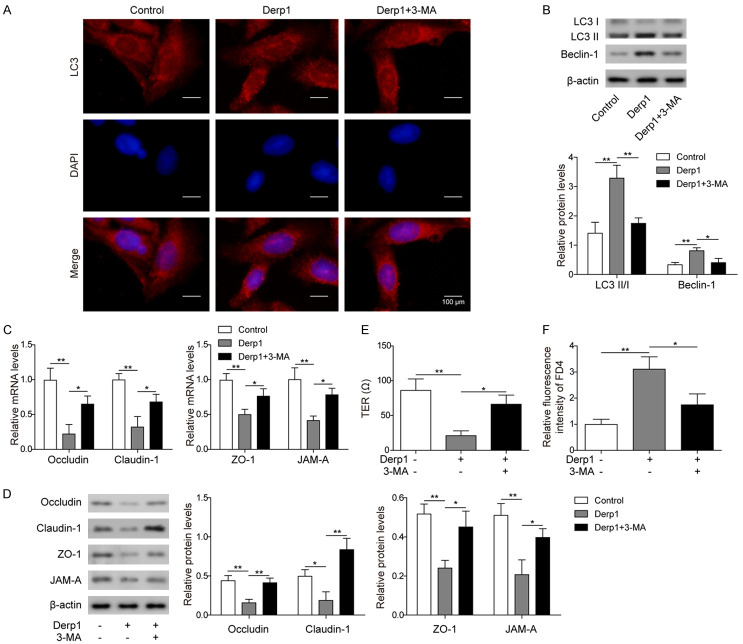
Figure 1.
Dust mite allergen (Derp1) promoted autophagy of nasal epithelial cells and damaged the function of the epithelial barrier. A. GFP-LC3 cells treated with PBS (Control), Derp1 (Derp1), or both Derp1 and 3-MA (Derp1+3-MA), LC3 expression was tested by fluorescence microscope. B. Western blot analysis of LC3 II/I and Beclin-1 in cells treated with PBS (Control), Derp1 (Derp1), or both Derp1 and 3-MA (Derp1+3-MA). C. qPCR measurements of Occludin, Claudin-1, ZO-1, and JAM-A in cells treated with PBS (Control), Derp1 (Derp1), or both Derp1 and 3-MA (Derp1+3-MA). D. Western blot analysis of Occludin, Claudin-1, ZO-1, and JAM-A in cells treated with PBS (Control), Derp1 (Derp1), or both Derp1 and 3-MA (Derp1+3-MA). E. TER measurement on cells treated with PBS (Control), Derp1 (Derp1), or both Derp1 and 3-MA (Derp1+3-MA). F. FD4 permeability assay in cells treated with PBS (Control), Derp1 (Derp1), or both Derp1 and 3-MA (Derp1+3-MA). Data were shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.