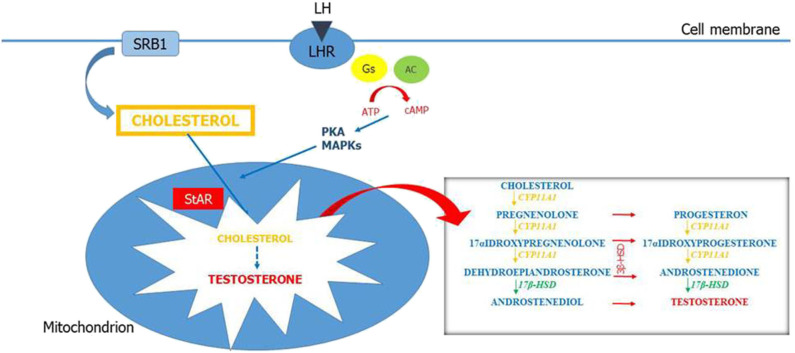
Figure 1.
Leydig cell steroidogenesis. LH binds to its receptors (LHR) on the Leydig cell (LC) membrane. This results in activation of Gs protein and adenylyl cyclase and increased concentration of intracellular cAMP. cAMP stimulates the mobilization and transport of cholesterol within the mitochondria in part by activating PKA and MAPK signaling. The first source of cholesterol for steroidogenesis is via uptake of cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoprotein (HDL) by the scavenger receptor SR-B1. Steroidogenic acute regulatory enzymes (StARs) regulate cholesterol transport from the outer to the inner mitochondrial membrane. At the inner mitochondrial membrane, cholesterol is converted into pregnenolone by CYP11A1 and pregnenolone is converted into testosterone by enzymes in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (3β-HSD, CYP17A1, and 17β-HSD).