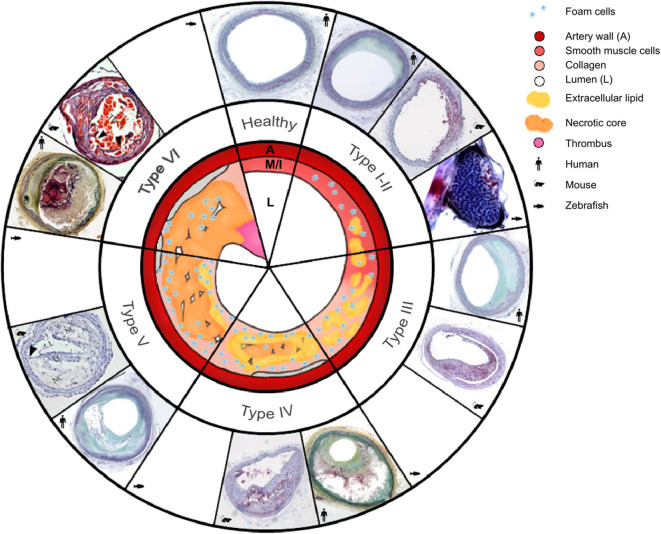
Figure 1.
Morphology of the six types of atherosclerosis in human, mouse, and zebrafish: a schematic overview with a comparison of micrographs. Healthy arteries have an adventitia surrounding the media (M), a very thin intima (I) layer, and a large lumen (L). As atherosclerosis initiates and progresses, different types are classified as follows: Type I, intima thickening; type II, fatty streaks, with or without macrophages; type III, intermediate lesion; type IV, advanced atheroma; type V, fibroatheroma; type VI, complicated plaques with surface defects, leading to plaque rupture. The type VI mouse lesion image shows an unstable plaque in the right common carotid artery in the tandem stenosis mouse model, and it is used to represent future mouse plaque rupture models. Micrographs representing human atherosclerosis, are from Yahagi et al. (2); micrographs of ApoE−/− mouse type I–IV atherosclerosis in the brachiocephalic artery and zebrafish belong to the Institute for Cardiogenetics. A set of micrographs of mouse types V and VI were taken from Chen et al. (3) Permission was granted for the use of all micropgraphs.