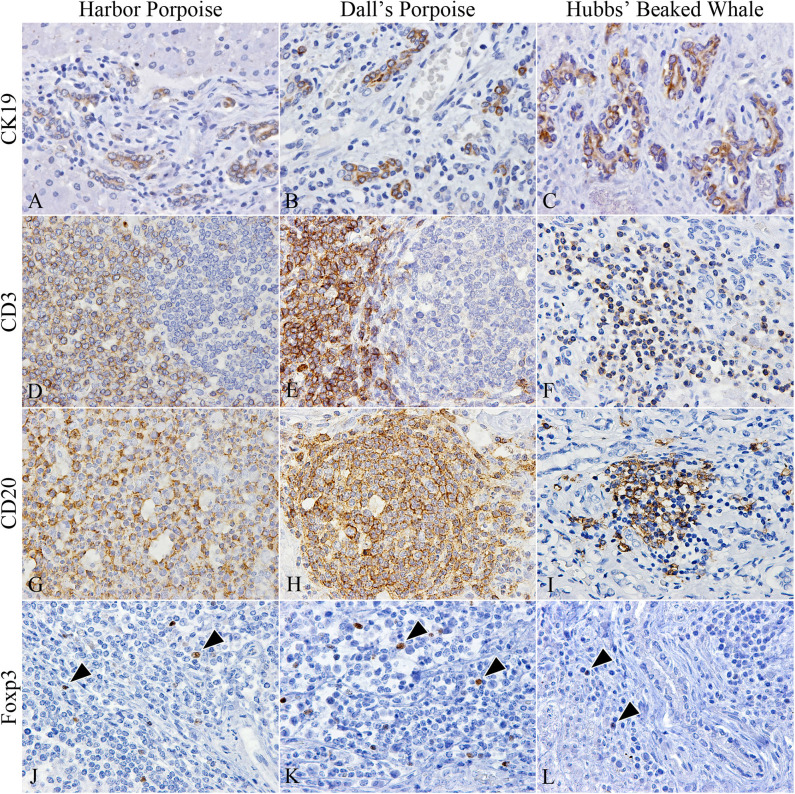
Figure 2.
Characterization of cholangiocytes and inflammatory cell populations in hepatic trematode infected livers of the harbor porpoise (left), Dall's porpoise (center), and Hubbs' beaked whale (right). (A–C) CK19-positive cholangiocytes are detected in areas of fibrosis, which form irregularly shaped hyperplastic bile ducts (A, case no. 3; B, case no. 14; C, case no. 18). (D–F) CD3-positive T cells are found in the paracortical areas of formed lymphoid follicles in the harbor porpoise (D, case no. 2) and Dall's porpoise (E, case no. 12), while it is more diffusely scattered within inflammatory infiltrates in the Hubbs' beaked whale (F, case no. 17). (G–I) Numerous CD20-positive B cells are detected within formed lymphoid follicles in the harbor porpoise (G, case no. 7) and Dall's porpoise (H, case no. 9), while the inflammatory infiltrates in the Hubbs' beaked whales have a mixed cell population (I, case no. 17). (J–L) Low numbers of Foxp3-positive regulatory T cells (arrowheads) are scattered within the inflammatory infiltrates of all three species (J, case no. 4; K, case no. 15; L, case no. 18).