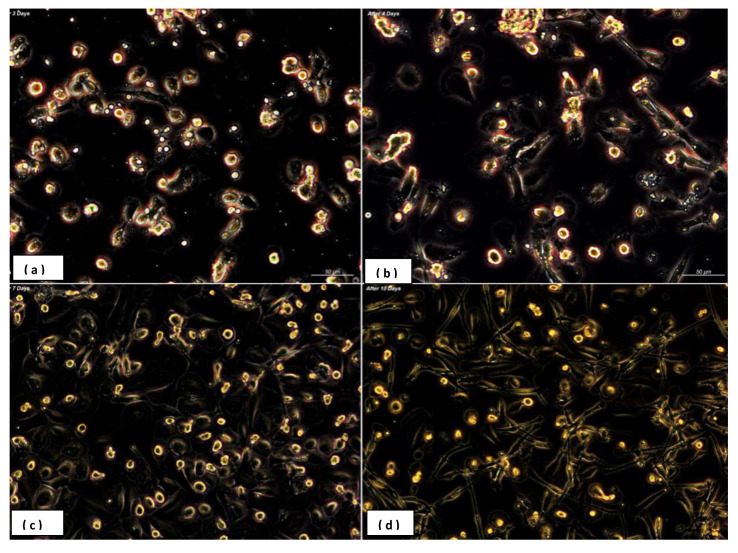
Figure 2.
Monocyte-derived macrophages presented a unique morphology dependent on performed stimulatory effect. Granulocyte/macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) led to a majority of elongated, fibroblast- spindle like shaped cells (c), and (d) similar to macrophages existent in lung alveoli, in contrast the presence of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) induced a majority of round or oval macrophages (fried eggs) like peritoneal macrophages (Axio observer Z1, Zeiss-AxioCamMR5 resolution 100×) (a,b). Human monocytes were cultured in RPMI-1640 with 20% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum supplemented with 5 ng/mL GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor) and 5 ng/mL M-CSF (macrophage colony- stimulating factor). Monocytes were differentiated for 10 days in the presence of M-CSF and GM-CSF cytokines. (a) At day 3, (b) at day 4 and (c,d) at day 7 and 10. After seven days monocytes differentiated into macrophages.