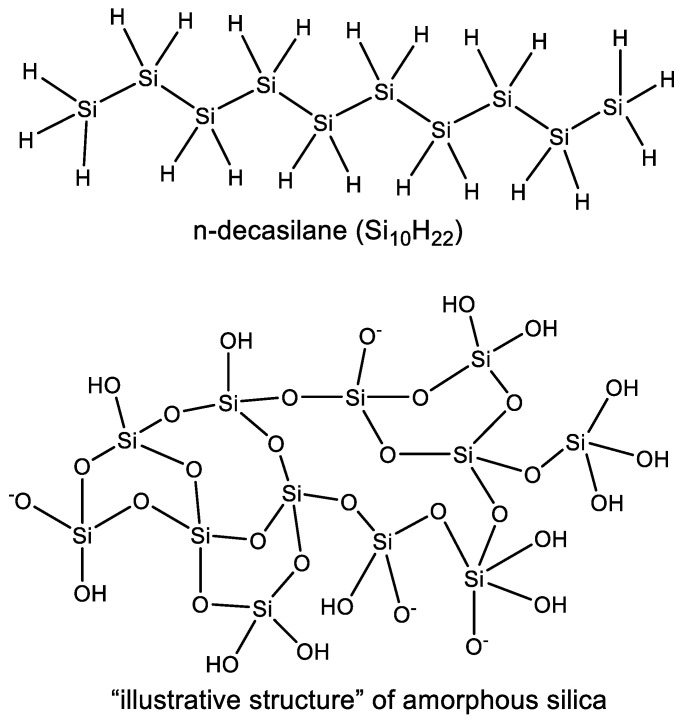
Figure 3.
Polymerization of silicon in oxygen-rich aqueous environments leads to a meshwork of Si–O chains (e.g., “illustrative structure” of amorphous silica) and not linear polymers like silanes (e.g., n-decasilane (Si10H22)). As a result, Si chemistry in oxygen-rich environments (e.g., water) ultimately leads to silica (SiO2), a refractory solid.