Fig. 1. Prediction results of two reading comprehension abilities (PVT and ORRT).
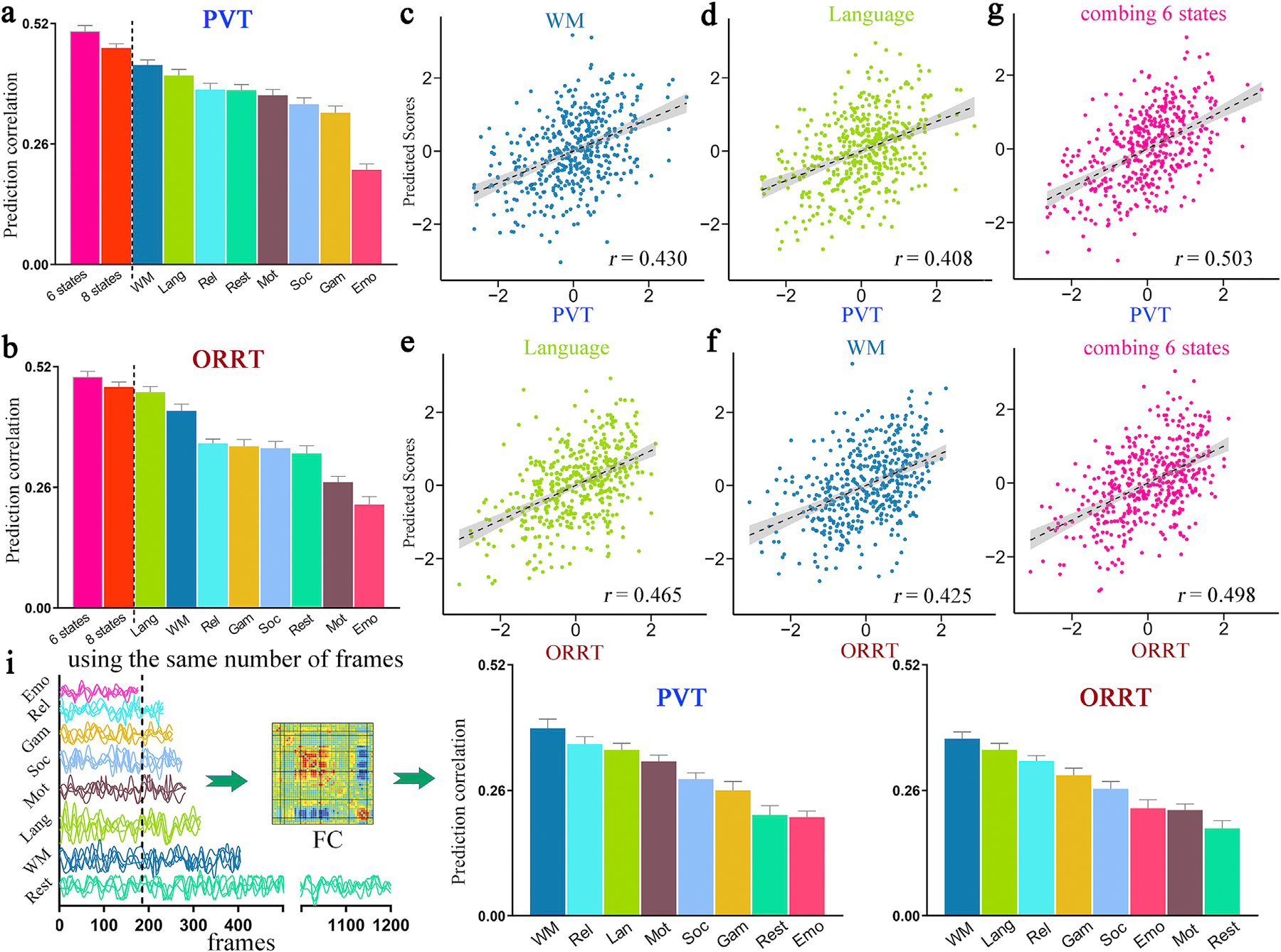
All 8 fMRI conditions yielded significant correlations between observed and predicted (a) PVT or (b) ORRT scores. Specifically, for PVT, the WM task yielded the best-performing model (c), and the language task yielded the second-best model (d). For ORRT, the language task achieved the highest prediction accuracy (e), and the WM task achieved the second-highest prediction accuracy (f). Combining FC features from all 8 fMRI conditions generated improved prediction performance (red bar in a, b) than using any single condition alone. An optimal combination of 6 cognitive conditions achieved the best predictions for both (g) PVT and (h) ORRT (r[PVT] = 0.503 ± 0.009, r[ORRT] = 0.498 ± 0.012; pink bar in a, b). Values in the x-axis and y-axis were normalized for visualization. (i) Given equal scan durations, all task-based models except emotion again achieved higher prediction accuracies than rest-based models. Abbreviation: Emo, emotion; Gam, gambling; Lang, language; Mot, motor; Rel, relational; Soc, social; WM, working memory; PVT, picture vocabulary test; ORRT, oral reading recognition test.
