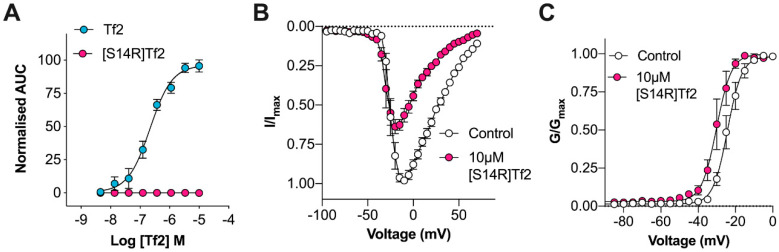
Figure 2.
Tf2[S14R] loses excitatory activity at hNaV1.3. (A) Comparative activity of Tf2 and Tf2[S14R] on hNaV1.3 assessed using the FLIPRTetra membrane potential assay. Tf2 (blue circles) concentration-dependently increased the membrane potential (EC50 213 ± 57 nM) while Tf2[S14R] (pink circles) had no effect up to 10 µM (n = 3–4 wells). (B) hNaV1.3 current–voltage relationship before (white circles) and after the addition of 10 μM Tf2[S14R] (pink circles). Tf2[S14R] decreased the peak current with a smaller effect on early channel opening compared to Tf2 (n = 5 cells). (C) hNaV1.3 conductance–voltage relationship before (white circles) and after the addition of 10 μM Tf2[S14R] (pink circles). Tf2[S14R] causes a smaller but significant (∆ −5.8 mV) hyperpolarizing shift in the voltage dependence of activation without affecting the slope factor (n = 5 cells). Data presented as mean ± SEM.