Fig. 6.
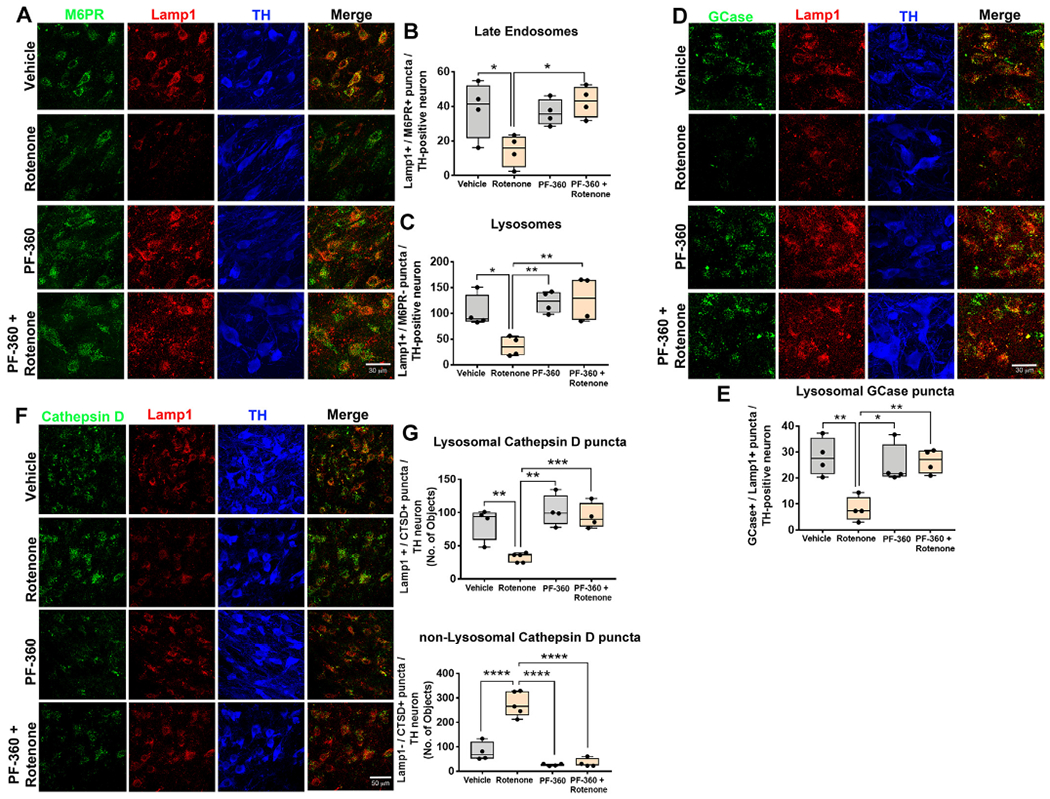
LRRK2 kinase inhibition prevented rotenone-induced endolysosomal deficits in rats. Endolysosomal deficits were assessed by immunohistochemistry in rats dosed with endpoint rotenone in the presence or absence of the LRRK2 kinase inhibitor PF-360. As shown, late endosomal (Lamp1+ and M6PR+) and lysosomal (Lamp1+ and M6PR−) puncta in rats treated with vehicle, PF-360 alone, endpoint rotenone alone or rotenone + PF-360. TH used as a marker of dopaminergic neurons. Representative photomicrographs for late endosomes and lysosomes in nigral dopaminergic neurons using M6PR (Green), Lamp1 (Red) and TH (Blue) (A). Quantification for the number of late endosomal and lysosomal puncta per nigral dopaminergic neuron; n = 4/grp (B–C). Lysosomal GCase (Lamp1+ and GCase+) in nigral dopaminergic neurons assessed by immunohistochemistry in rats dosed with endpoint rotenone in the presence or absence of the LRRK2 kinase inhibitor PF-360. As shown, representative photomicrographs of GCase (Green), Lamp1 (Red) and TH (Blue) in rats treated with vehicle, PF-360 alone, endpoint rotenone alone or rotenone + PF-360 (D). Quantification for the number of lysosomal GCase puncta per nigral dopaminergic neuron; n = 4/grp (E). Lysosomal and non-lysosomal cathepsin D immunoreactivity assessed in nigral dopaminergic neurons using specific markers. Representative photomicrographs for lysosomal cathepsin D (cathepsin D+ , Lamp 1+) and non-lysosomal (cathepsin D+ , Lamp 1−) puncta in nigral dopaminergic neurons using cathepsin D (Green), Lamp1 (Red) and TH (Blue) (F). Quantification for average number of cathepsin D puncta per nigral dopaminergic neuron; n = 4/grp (G). Data are analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc analysis. * p < .05, ** p < .01, graphs are expressed as mean ± SEM. Symbols represent individual brains. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
