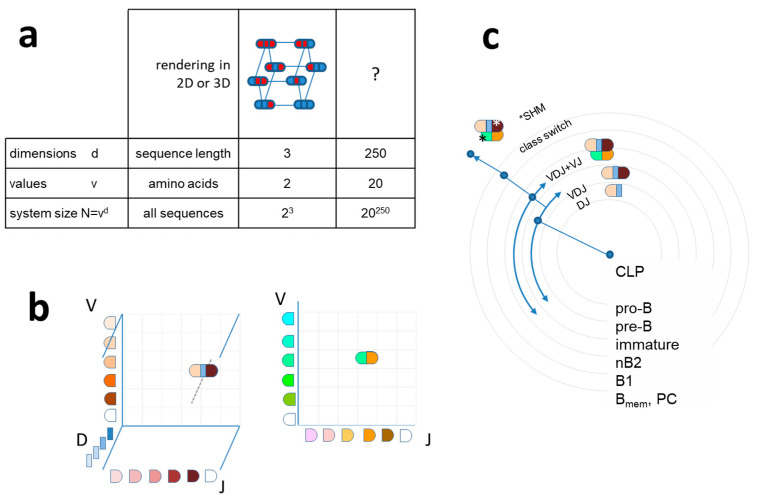
Figure 1.
Sequence space and visualization of antibody sequence relationships (a) Theoretical diversity (system size N) of a sequence is determined by its length (dimension) and the number of values a particular position in the sequence can take. An antibody Fv region of 250 amino acids has an astronomical sequence diversity if full randomization is allowed. (b) Antibody sequences are frequently interpreted as recombined germline sequences. Such display of combinatorial diversity may allow the tracking of specific clonal expansions and further diversification by somatic hypermutation (SHM). (c) The potential development scheme of a given antibody clone is shown with antibody sequence development along with B-cell differentiation steps. Arching arrows represent combinatorial diversification by V–D–J rearrangement and light chain paring. CLP, common lymphoid progenitor; nB2, naïve B2 cell; Bmem, memory B cell; PC, plasma cell.