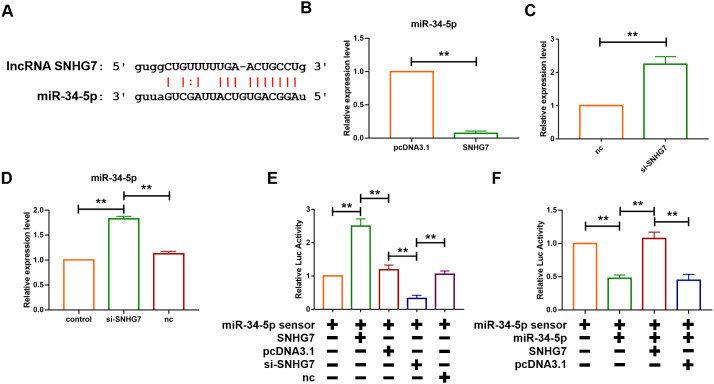
Figure 3.
lcnRNA SNHG7 acted as a ceRNA and sponged miR-34-5p. (A) The predicted binding sites of SNHG7 and miR-34-5p. (B) Forced expression of SNHG7 with a SNHG7 expression plasmid inhibited the expression of miR-34-5p in cardiac fibroblasts. U6 served as an internal control. Data was presented as mean ± SEM; two-tailed t test was used for the statistical analysis. n=5 independent cell cultures. (C) Knockdown of SNHG7 by its siRNA increased the expression of miR-34-5p in cardiac fibroblasts. U6 served as an internal control. Data was presented mean ± SEM; two-tailed t test was used for the statistical analysis. n=5 independent cell cultures. (D) Knockdown of SNHG7 increased the expression of miR-34-5p in normal mice. U6 served as an internal control. Data was presented mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA was used for the statistical analysis. n=6 mice per group. (E) SNHG7 binds to miR-34-5p and inhibits its activity. Cardiac fibroblasts were co-transfected with the miR-34-5p sensor and SNHG7 or si-SNHG7 and its corresponding scrambled form, and luciferase activity was detected. Data was presented as mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA was used for the statistical analysis. n=5 independent cell cultures. (F) Cardiac fibroblasts were co-transfected with the miR-34-5p sensor and miR-34-5p or SNHG7 and its corresponding scrambled form, and luciferase activity was determined. Data was presented as mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA was used for the statistical analysis. n=5 independent cell cultures. **P<0.05.