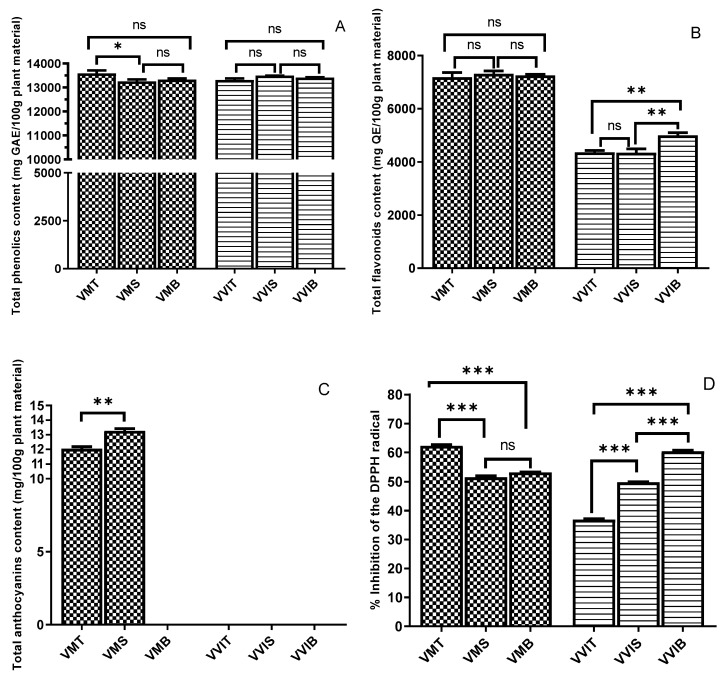
Figure 1.
Total phenolic content (Folin–Ciocalteu method) (A), total flavonoids content (B), total anthocyanin content (C), and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) antioxidant activity (D) of the two species leave extracts, from all three locations. The total phenolic content of the extract is expressed as gallic acid equivalents (GAE) in mg/100 g plant material. Total flavonoid content is expressed as quercetin equivalents (QE) in mg/100 g plant material. The DPPH activity was expressed as percentage inhibition (I%). Values are reported as mean ± SD of triplicate determinations and different symbols (*, **, ***) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between the three different locations for each of the two species leave extracts, separately (one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), multiple comparison tests, Tukey multiple range tests), while symbol (ns) indicate no significant difference. VMT, V. myrtillus leaves from Turda; VMS, V. myrtillus leaves from Smida; VMB, V. myrtillus leaves from Borsa; VVIT, V. vitis-idaea leaves from Turda; VVIS, V. vitis-idaea leaves from Smida; VVIB, V. vitis-idaea leaves from Borsa.