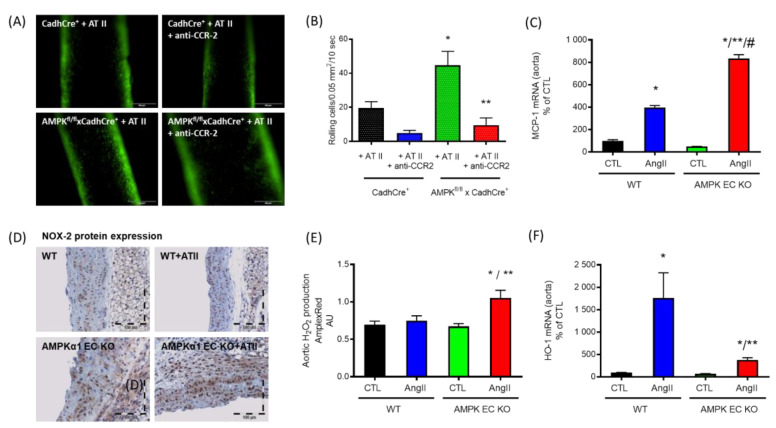
Figure 3.
Functions of endothelial specific α1AMPK. (A,B) Epifluorescence intravital microscopy was used to visualize adherent and rolling leucocytes in carotid arteries. Nucleated cells were stained with acridine orange (green fluorescence). Representative images of carotid arteries are shown after 7 days of continuous AT II infusion (n = 8) before and 60 min after single intraperitoneal injection of anti-CCR2 antibody (anti-CCR2). Deletion of endothelial-specific α1AMPK (AMPKfl/fl×CadhCre+ + AT II) leads to a loss of endothelial barrier function and an enormous AT II-induced increase in CCR-2-dependent recruitment of inflammatory cells to the vascular wall in comparison with the wild-type littermates (CadhCre+ + AT II) that was prevented by anti-CCR2 treatment. * p < 0.05 vs. CadhCre+ + AT II, ** p < 0.05 vs. AMPKfl/fl×CadhCre+ + AT II. (C) mRNA expression of MCP-1 was significantly upregulated in aortic tissue of AT II-treated mice lacking α1AMPK in the endothelium (n = 6), which was accompanied by immune cell infiltration and (D) increased NOX-2 protein measured by immunohistochemistry (brown staining) (n = 4). (E) Furthermore, oxidative stress, measured by Amplex Red assay (n = 4), was significantly increased in mice lacking the endothelial α1AMPK treated with AT II. (F) In addition to this, the loss of endothelial α1AMPK impaired the antioxidant defense induced normally by AT II (n = 11). * p < 0.05 vs. WT CTL, ** p < 0.05 vs. WT AngII, # p < 0.05 vs. AMPK EC KO CTL. Data were reused from [94] with permission. Copyright © 2019, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature. Abbreviations: AMPK EC KO: TekCre-specific AMPK deletion (AMPKfl/flxTekCre+); AMPK: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; AT II: angiotensin II; CCR-2: C-C motif chemokine receptor 2; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; H2O2: hydrogen peroxide; NOX-2: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 2; MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1.