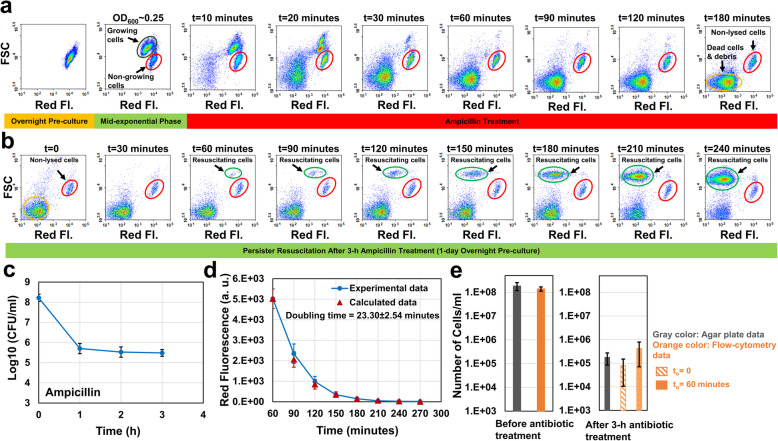
Fig. 2.
Monitoring persister resuscitation. a Exponential-phase cells at OD600 = 0.25 (prepared from 1-day overnight pre-cultures) were treated with 60 μg/ml ampicillin for 3 h in the presence of IPTG. Cells during the treatment were collected at designated time points and analyzed by a flow cytometer. b After 3-h ampicillin treatments, cells were collected and washed to remove the antibiotic and the inducer. The cells were then resuspended into fresh LB broth and cultured. At designated time points, samples were collected to be analyzed with a flow cytometer to monitor persister resuscitation (N = 4). c Cells during the antibiotic treatment were plated on agar media at designated time points for CFU enumeration (N = 4). d The doubling time of the resuscitating cells was calculated using the decay equation (see the Materials and Methods) and the mean red fluorescence intensities of dividing cells (highlighted with light green circles) (N = 4). e Resuscitating cell levels (number of cells per 1 ml culture medium) after 3-h antibiotic treatments were estimated from the standard agar plating method (gray column) and the flow-cytometry analysis (assuming to = 0 and to = 60 min; patterned orange columns). Cells were also counted before the antibiotic treatments. Growing, non-lysed, dead (debris) and resuscitating cell subpopulations are highlighted with dark green, red, orange and light green circles, respectively. The flow-cytometry diagrams are a representative replicate of four independent biological replicates. Error bars represent the standard deviations