Figure 1.
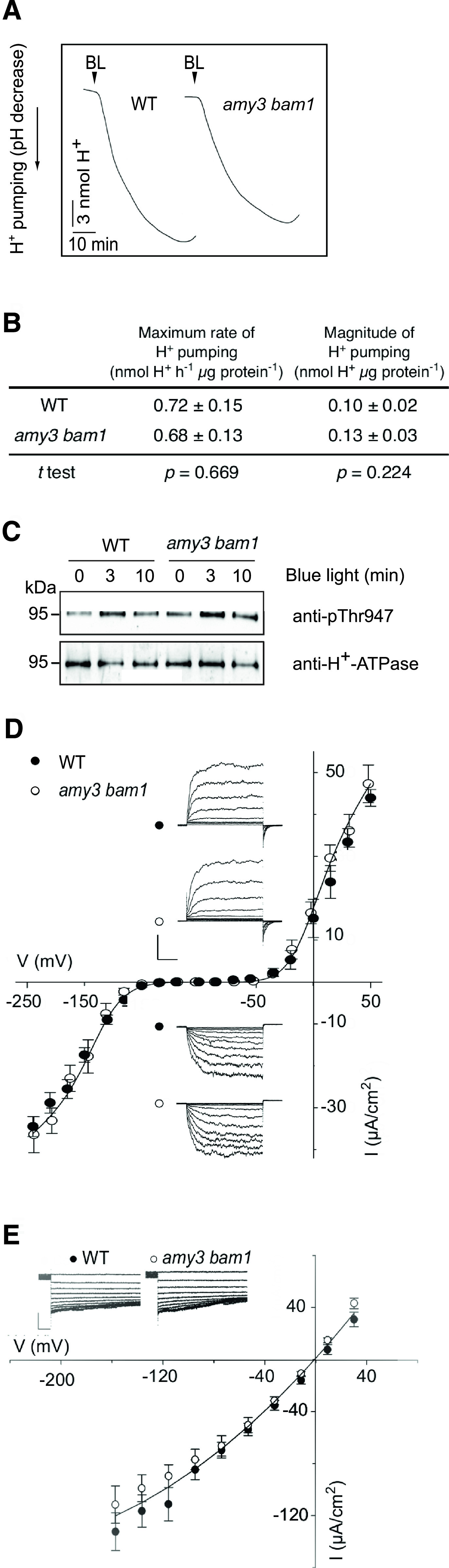
Membrane Ion Transport in Wild-Type and amy3 bam1 Guard Cells.
(A) BL-dependent H+ pumping in GCPs. GCPs were exposed to RL (50 μmol m−2 s−1) for 2 h, after which BL (10 μmol m−2 s−1) was applied for 30 min. One representative experiment out of five experiments is shown. WT, wild type.
(B) BL-dependent H+ pumping quantification. Values represent means ± se (n = 5).
(C) Immunoblots of BL-dependent H+-ATPase phosphorylation in GCPs. The upper blot displays the detection of the phosphorylation level of the H+-ATPase by immunoblot using the anti-phospho-Thr947 antibody (p-Thr). The lower blot shows detection of the H+-ATPase using a specific antibody against the C terminus of the H+-ATPase. Each lane contained 1.5 to 3.5 μg of guard cell proteins.
(D) Steady-state currents recorded under voltage clamp for IK,in and IK,out in isolated guard cells. Solid curves are fittings of the wild type (n = 8) and amy3 bam1 (n = 8) to a Boltzmann function. Data are mean ± se. The insets show measurements that were typically obtained by clamping in cycles with a holding voltage of −100 mV and 6-s steps either to voltages from −120 to −240 mV for IK,in or voltages from −80 to +40 mV for IK,out.
(E) Instantaneous current voltage curves for ICl recorded in the wild type (n = 8) and amy3 bam1 (n = 11). Data are means ± se. Solid curve shows an empirical fitting to the second-order polynomial function and is included for clarity. The insets show representative ICl traces during 7-s clamp steps to voltages from +30 mV to −160 mV after a 10-s clamp step at +30 mV.
