Figure 8.
Modeling of the Impact of the RNAi Transgene on the Embryonic Cells of B. napus.
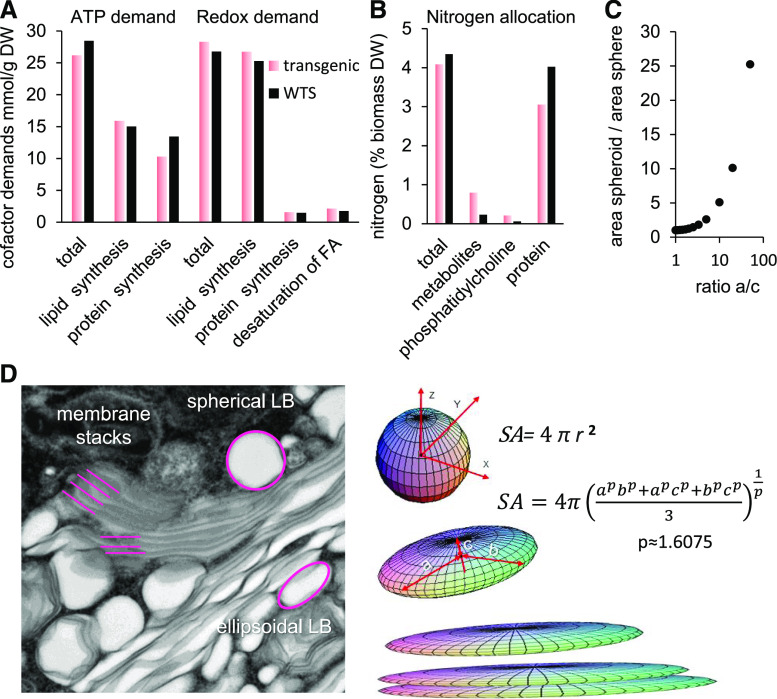
(A) Demands in energy cofactors (ATP and reducing equivalents) for the biosynthesis of proteins and lipids. The reducing equivalents for fatty acid desaturation are shown separately of the balance for lipids. Details are given in Supplemental Data Set 5E. DW, dry weight.
(B) Allocation of nitrogen among different biomass fractions (based on biomass and elemental composition in Supplemental Data Set 5C).
(C) Increase of surface area in response to ellipsoid parameters. Increasing one of the axes of a sphere while keeping its volume constant will result in an increase of the surface area of the ellipsoid over the sphere. Calculation was based on the formula in (D).
(D) Gain of surface by reshaping lipid bodies (LB). The left panel shows distinctly shaped lipid bodies in an electron micrograph. The right panel exemplifies how the transition from sphere to ellipsoid (at constant volume) causes tremendous gain in surface area (SA). Transgenic embryonic cells apply this strategy to incorporate the excess membrane protein oleosin; the stacks are partially a consequence of the excess oleosin and the preponderance of phospholipid at the partial expense of TAGs.