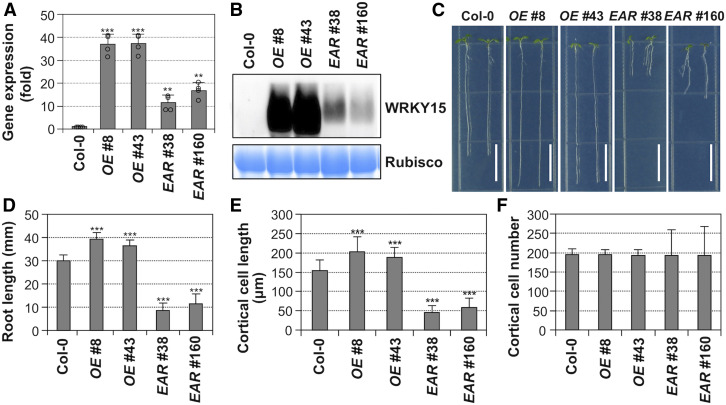
Figure 2.
Overexpression and Dominant-Negative Suppression of WRKY15 Transgenic Seedlings Have Opposite Effects on Root Elongation.
(A) Wild-type (Col-0), WRKY15 overexpression (WRKY15OE, lines no. 8 and no. 43), and WRKY15 dominant-negative suppression (WRKY15-EAR, lines no. 38 and no. 160) transgenic seedlings were cultured vertically on 1/2 MS plates under continuous light, and roots of 5-d-old seedlings (>50) were collected for total RNA preparation. Expression levels of transgenes were quantified by real-time qPCR and normalized to UBQ10. Error bars represent the standard deviations (n = 4).
(B) Total proteins from Col-0 and transgenic seedlings were extracted, levels of transgene expression were detected by immunoblot analysis using an anti-myc antibody (top), and equal loading was confirmed by Coomassie brilliant blue–stained gels (bottom).
(C) Root elongation phenotypes of WRKY15OE (lines no. 8 and no. 43) and WRKY15-EAR (lines no. 38 and no. 160) seedlings.
(D) Quantitation of primary root length of each genotype. Error bars indicate SD (n = 30).
(E) and (F) Root elongation phenotypes of WRKY15OE and WRKY15-EAR seedlings are associated with altered cell elongation (E), but not cell number (F). More than 500 mature root cortical cells from 20, 7-d-old seedlings were measured to determine the cell length and cell number per millimeter of root length. A significant difference is indicated by asterisks above the columns (One-way ANOVA, ***P < 0.001). Scale bar = 1 cm.