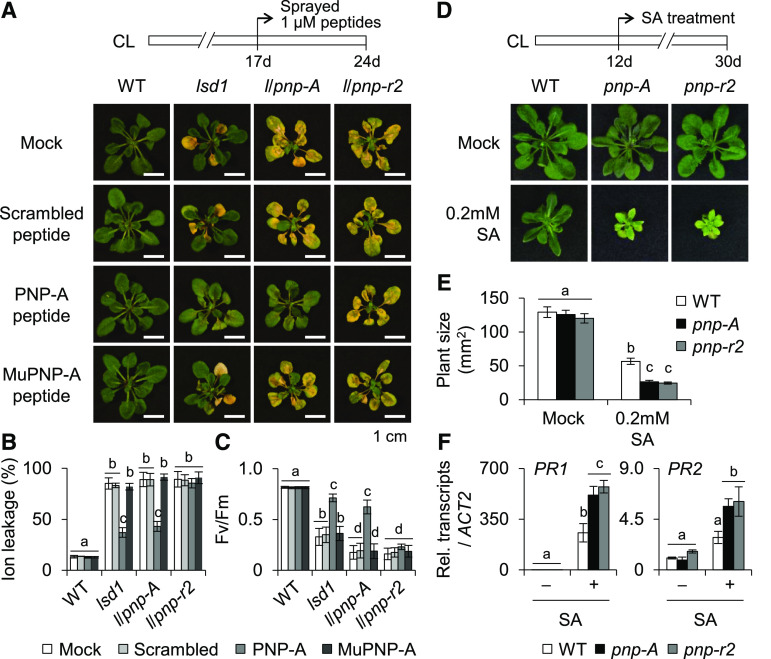
Figure 7.
pnp-r2 Mutant Plants Are Insensitive to PNP-A and Hypersensitive to SA.
(A) to (C) Seventeen-day-old wild-type (WT), lsd1, lsd1 pnp-A, and lsd1 pnp-r2-2 plants grown under CL were treated with 1 µM scrambled, active (PNP-A), or mutated (MuPNP-A) form of AtPNP-A synthetic peptide and kept for 7 d under CL. Afterward, the RCD phenotype (A), ion leakage (B), and Fv/Fm (C) were examined. The representative images are shown at the same scale. For the measurement of Fv/Fm, 10 leaves per genotype were used. Value in (B) represents means ± sd (n = 3).
(D) and (E) Twelve-day-old wild-type (WT), pnp-A, and pnp-r2-2 plants grown on MS medium under CL were transferred to MS medium in the absence (Mock) or presence of 0.2 mM SA and kept for 18 d under same growth condition. The representative foliar phenotype (D) and plant size (E) of each genotype are shown. For the measurement of plant size, 15 plants per genotype were used. Value represents means ± sd (n = 15).
(F) Plants of the indicated genotypes grown under CL for 14 d were sprayed with either a 0.5 mM SA solution (+SA) or a mock solution (–SA), and foliar tissues were collected 6 h after the treatment. Expression levels of PR1 and PR2 were examined by RT-qPCR. ACT2 was used as an internal standard. Value represents means ± sd (n = 3). Lowercase letters in (B), (C), (E), and (F) indicate statistically significant differences between mean values (P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s honestly significant difference [HSD] test; Supplemental Data Set).