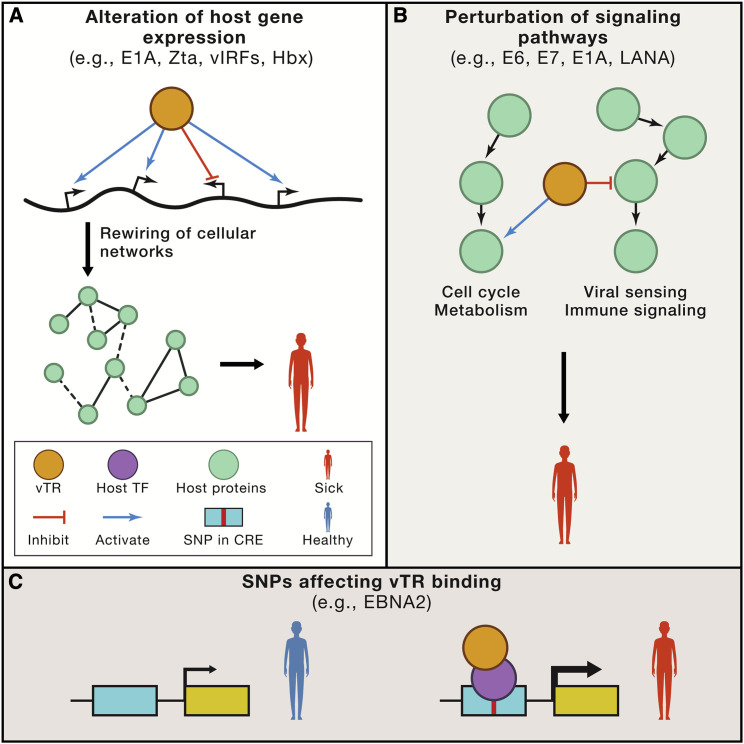
Figure 3.
Roles for vTRs in Human Diseases
(A) vTRs can alter host gene expression, resulting in cellular network rewiring, ultimately leading to disease.
(B) vTRs can perturb signaling pathways through protein-protein interactions or enzymatic activities. This includes the inhibition of pathways involved in viral sensing and immune signaling, and activating cell cycle progression and cell metabolism. Such perturbations can lead to cancer and other diseases.
(C) Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and other genetic variants can affect vTR binding, either directly or indirectly through altered host TF binding. This can lead to changes in target gene expression, ultimately leading to disease. CRE, cis regulatory element.