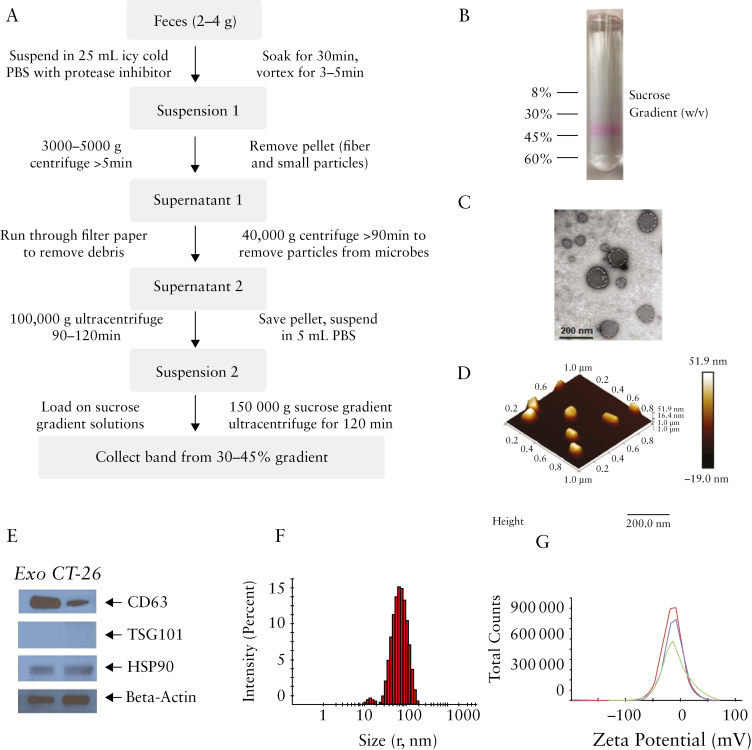
Figure 1.
Isolation of intestinal exosomes. [a] Workflow for isolating intestinal exosomes from faeces. [b] A protein dye [Ponceau S] is used to visualise the exosomes, and intestinal exosomes are collected by 30–45% sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation. [c] Electron microscopy of intestinal exosomes. [d] Atomic force microscopy of intestinal exosomes. [e] Western blotting of protein biomarkers for intestinal exosomes [CD-63, TSG101, and HSP90] and control [Colon-26 cell secreted] exosomes. [f] Size [radius, ~70 nm] and surface zeta potential [~-12 mV] of intestinal exosomes.