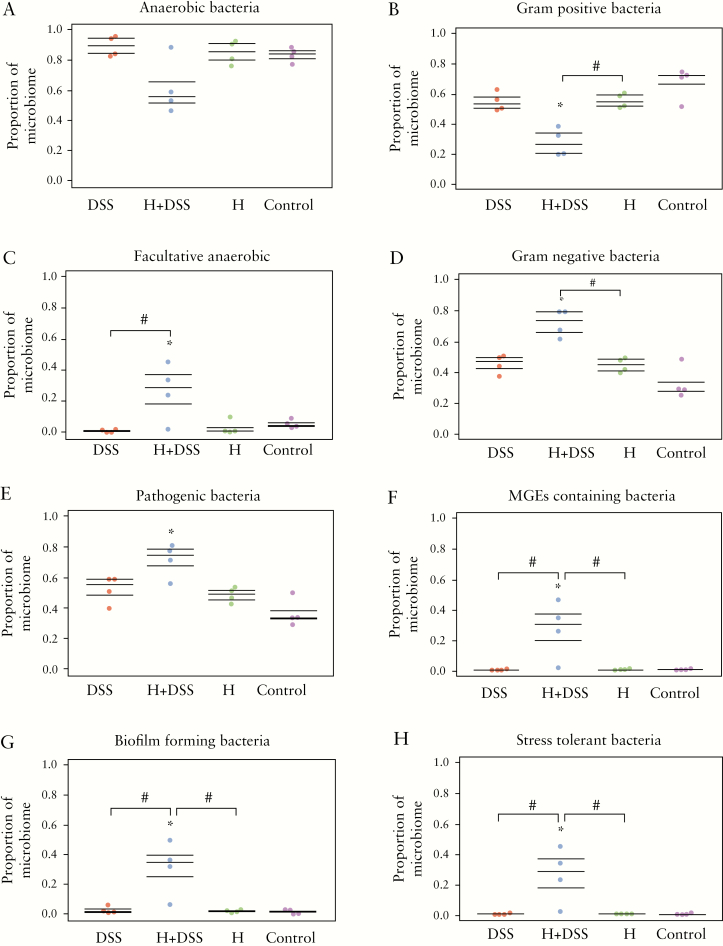
Figure 6.
Hydromorphone induces functional phenotypic alterations in gut microbiota in DSS-treated mice. Predicted metagenomic functional analysis was performed by using BugBase software package. Hydromorphone plus DSS treatment results in decrease in [A] anaerobic bacteria, and [B] Gram-positive bacteria, whereas significant increase in [C] facultative anaerobic, [D] Gram-negative, [E] pathogenic, [F] MGEs-containing, [G] biofilm-forming, and [H] stress tolerant bacteria [n = 4 per group]. Mean ± SEM, 95% CI. Asterisk [*] indicates statistical significance [p <0.05] vs control group and hash sign [#] indicates statistical significance [p <0.05] between treatment groups by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. DSS, dextran sulphate sodium; MGEs, mobile genetic elements; SEM, standard error of the mean; CI, confidence interval; ANOVA, analysis of variance.