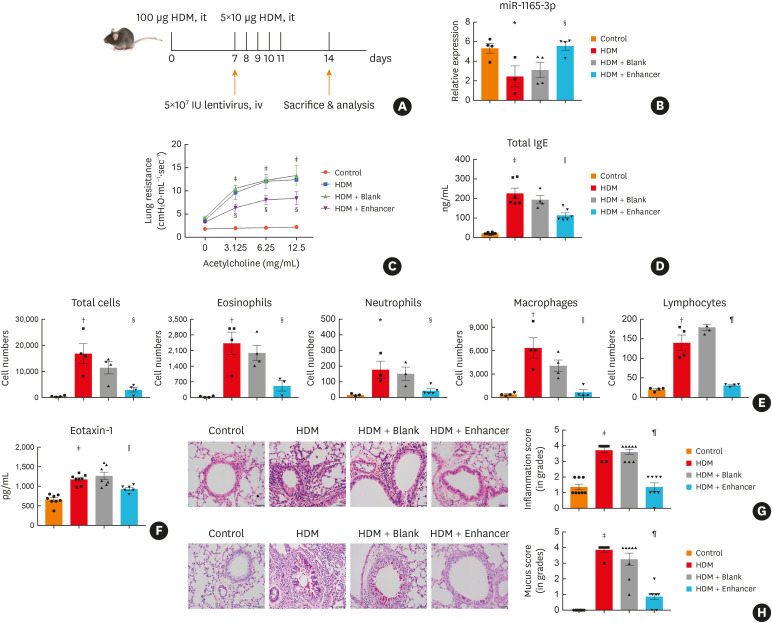
Fig. 3. MiR-1165-3p inhibited allergic airway inflammation. (A) Experimental design of the study. (B) The level of miR-1165-3p in different groups. (C) Mice inhaled increasing doses of acetylcholine (0–12.5 mg/mL), and AHR was measured. (D) The concentration of IgE was measured by ELISA. (E) Total and differential cell counts in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were determined by flow cytometry. (F) The concentrations of eotaxin-1 in lung homogenates were measured with ELISA (G) Lung sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin stain to analyze the infiltration of inflammatory cells, and the severity of peribronchial inflammation was graded semiquantitatively. (H) Lung sections were stained with PAS to assess goblet cell hyperplasia, PAS-positive and PAS-negative epithelial cells were counted, and the percentage of PAS-positive cells per bronchiole was calculated. Scale bar, 50 μm (n = 3–8).
HDM, house dust mite; miR-1165-3p, microRNA-1165-3p; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; AHR, airway hyperreactivity; IgE, immunoglobulin E; PAS, periodic acid-Schiff.
*P < 0.05, †P < 0.01, ‡P < 0.001, HDM vs. control group; §P < 0.05, ‖P < 0.01, ¶P < 0.001, HDM + enhancer vs. HDM + blank group.