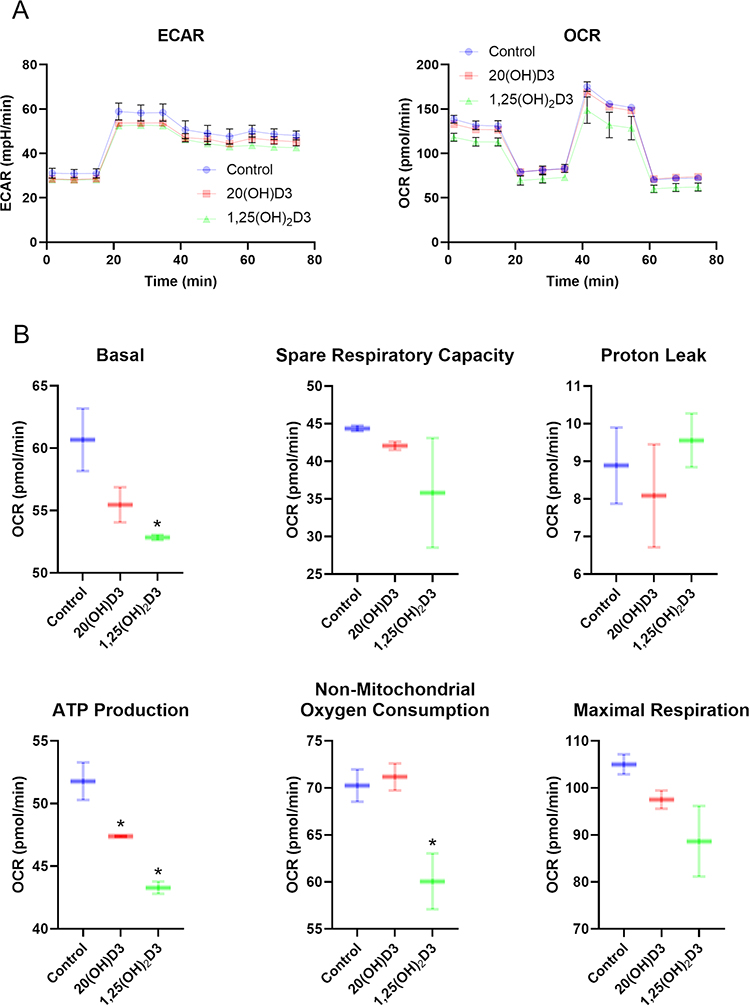
Figure 4.
The effects of vitamin D3 derivatives on mitochondrial function. A, Representative traces of mitochondrial oxygen consumption rates (OCR) and, extracellular acidification rates (ECAR) in control (vehicle), 100n M 20(OH)D3 or 1,25(OH)2D3-treated HaCaT cells. B, Indices of mitochondrial function include basal, ATP-linked, maximal, reserve capacity, proton leak, and nonmitochondrial oxygen consumption rates. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 2. *P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test).
A Seahorse XFe24 Analyzer (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA) was used to determine ATP production rates, extracellular acidification rates (ECAR) and oxygen consumption rates (OCR). An XF Real-Time ATP Rate Assay Kit and an XF Cell Mito Stress Test Kits were used according to the manufacture’s protocol. HaCaT cells were cultured on a XF Cell Culture Microplate in DMEM media containing 5% charcoal-stripped FBS for 24 h followed by treatment with vitamin D3 derivatives, as indicated, for 24 h. Next, cells were washed with assay media and incubated for 60 min prior to OCR and ECAR assays.