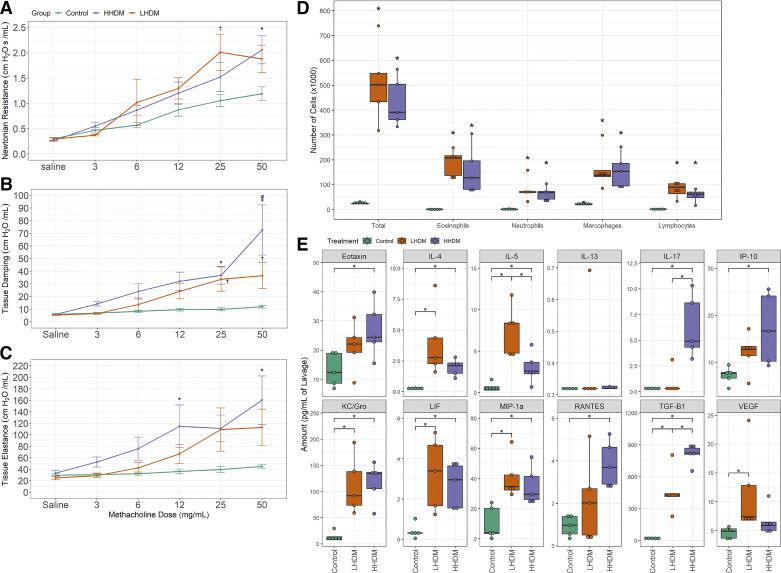
Fig. 2.
House dust mite (HDM) endotoxin abundance alters lung function and inflammatory parameters in the female murine lung. A–E: Newtonian resistance (A), tissue damping (B), tissue elastance (C), lavage differential cell counts (D), and inflammatory cytokines (E) in lavage (normalized to lavage volume). For lung function data, maximum values in response to methacholine were collected. Lung function (A–C): *P < 0.05, high-endotoxin HDM (HHDM) vs. control mice; †P < 0.05 LHDM vs. control mice; #P < 0.05 vs. LHDM challenged mice (repeated measures two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons between groups). Differential cell counts (D): *P < 0.05 vs. control mice (two-way ANOVA with Tukey comparison between groups). Cytokine abundance (E): *P < 0.05 (MANOVA); n = 5 female mice per treatment group. Green: control; orange: low-endotoxin HDM; purple: high-endotoxin HDM.