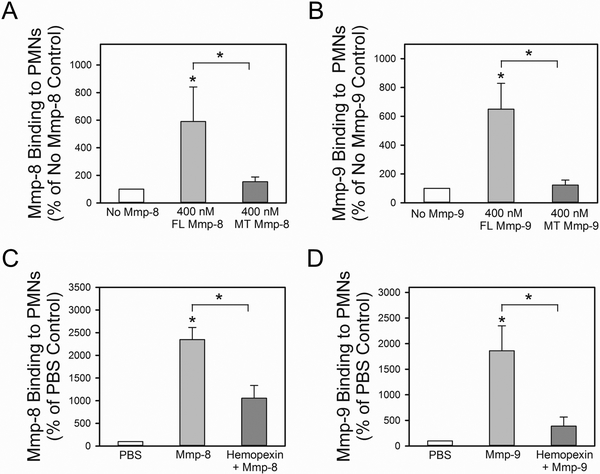
Figure 8: The COOH-terminal hemopexin domain of both proMmp-8 and proMmp-9 is required for the binding of these proteinases to the surface of activated PMNs:
In A, PAF- and fMLP-activated Mmp-8−/− x Mmp-9−/− PMNs were incubated for 2 h at 4°C with or without 400 nM full length proMmp-8 protein (FL Mmp8) or 400 nM mutant proMmp-8 protein lacking the COOH-terminal hemopexin domain (MT Mmp-8). Bound Mmp-8 was detected by immunostaining cells with Alexa 488 using an antibody raised to the hinge region of Mmp-8 (which is present in both the FL and MT forms of Mmp-8). In B, PAF- and fMLP-activated Mmp-8−/− x Mmp9−/− PMNs were incubated for 2 h at 4°C with or without 400 nM full length Mmp-9 (FL Mmp9) or 400 nM mutant Mmp-9 lacking the COOH-terminal hemopexin domain (MT Mmp9). Bound Mmp-9 was detected by immunostaining cells with Alexa 488 using an antibody raised to the hinge region of Mmp-9 (which is present in both the FL and MT forms of Mmp-8 and Mmp-9). In A-B, Data are mean + SEM; n = 3 separate experiments each analyzing 300 cells/group). Data were analyzed using a One-Way ANOVA followed by pair-wise testing with two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Asterisk indicates P < 0.05 compared with the no exogenous Mmp group or the group indicated. In C-D, PAF- and fMLP-activated Mmp-8−/− x Mmp9−/− PMNs were incubated at 4°C for 60 min with or without 500 nM soluble murine hemopexin protein. Cells were then incubated at 4°C for 60 min with or without 400 nM exogenous proMmp-8 or 400 nM exogenous proMmp-9. Mmp-8 and Mmp-9 that bound to cells was detected by immunostaining the cells with Alexa-488 for Mmp-8 (C) or Mmp-9 (D), as described above. Data are mean + SEM; n = 3 separate experiments each analyzing 300 cells/group. Data were analyzed using a One-Way ANOVA followed by pair-wise testing with two-tailed Student’s t-tests. Asterisk indicates P < 0.05 compared with the group incubated without exogenous proteins or the group indicated.