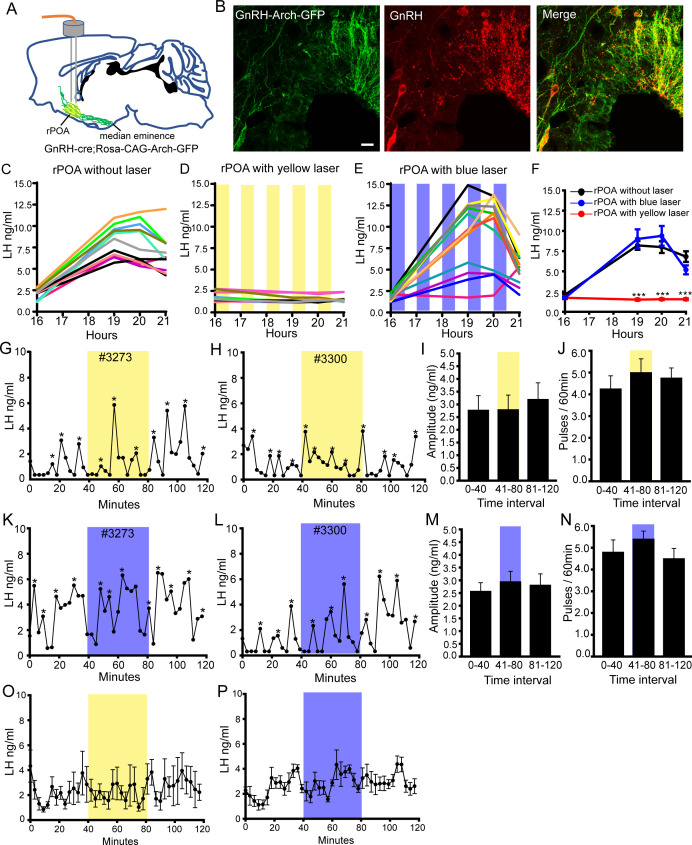
Figure 5. Bilateral optogenetic inhibition of GnRH neuron soma-proximal dendrite activity suppresses only the LH surge.
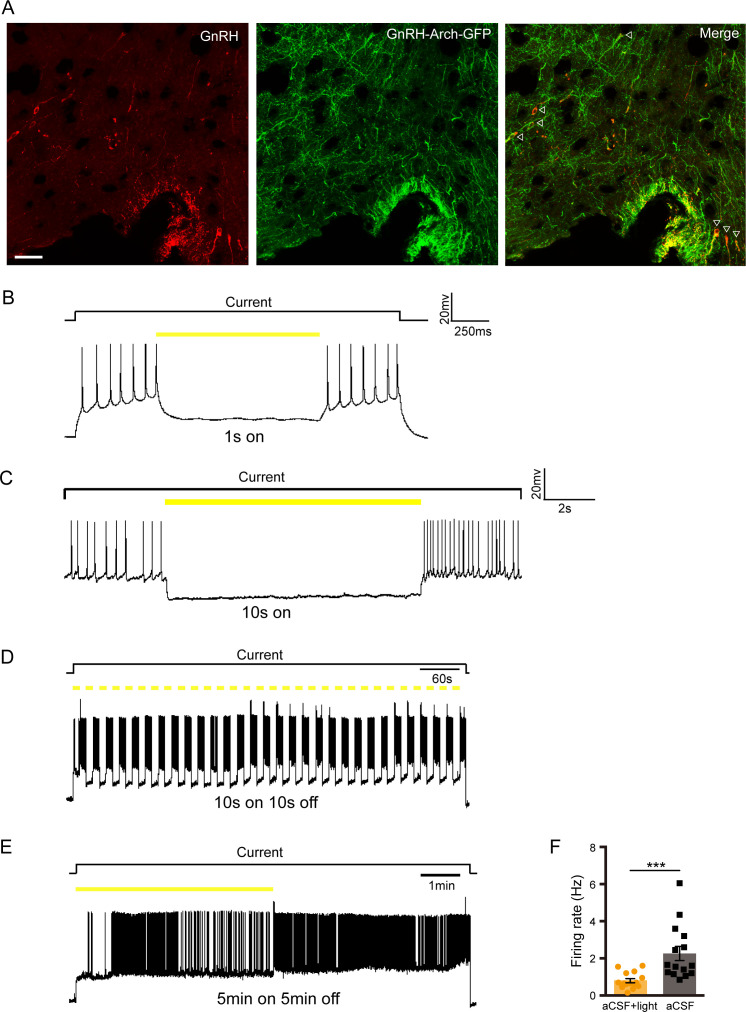
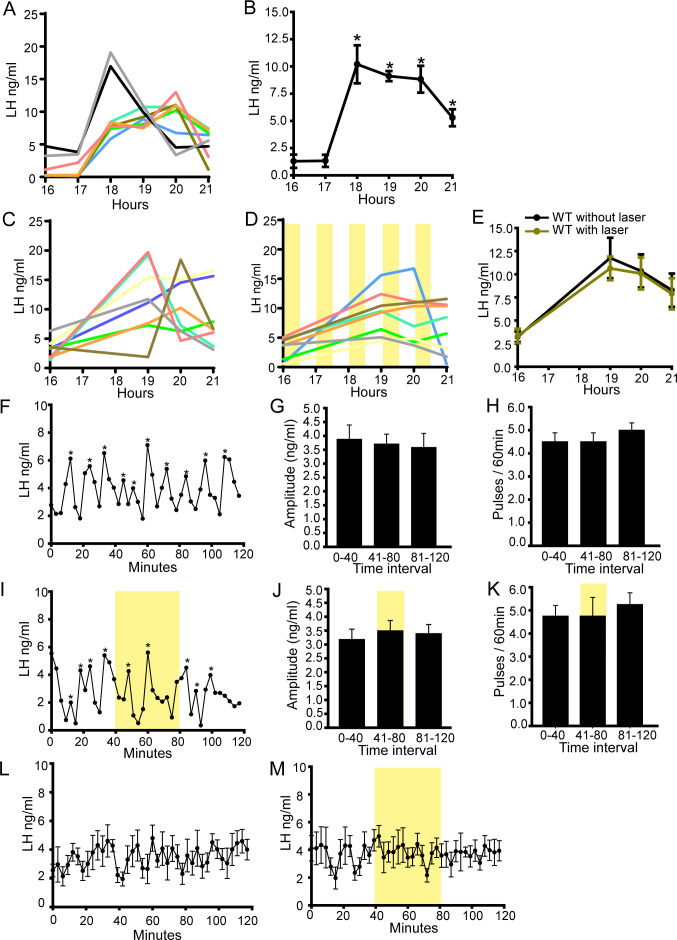
(A) Schematic showing experimental protocol with GnRH-cre+/-;Rosa-CAG-Arch-GFP+/+ mice with bilateral optic fiber placement in the rostral preoptic area (rPOA). (B) Fluorescence images of GnRH neurons expressing Archaerhodopsin (GFP reporter) and GnRH (red) in GnRH-cre+/-;Rosa-CAG-Arch3-GFP+/+ mice. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C-E) LH surge profiles in all control GnRH-cre+/-;Rosa-CAG-Arch-GFP+/+ OVX+E+P female mice (C, n = 11) and those given intermittent (yellow shaded areas) bilateral rPOA 593 nm illumination at 10 Hz (D, n = 12) or, as a control, 473 nm (E, n = 12). (F) Mean (± SEM) LH levels. ***p<0.001, two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Holm-Sidak test. (G-N) Representative profiles of pulsatile LH secretion in GnRH-cre+/-;Rosa-CAG-Arch3-GFP+/+ OVX female mice given 40 min (shaded areas) bilateral rPOA illumination at 593 nm (G, H) or, as a control, 473 nm (K, L). LH pulses are indicated by asterisks. Mean (± SEM) LH pulse amplitude and frequency are given for yellow (I,J, n = 7) and blue (M,N, n = 6) light illumination. (O,P) Mean (± SEM) LH levels in GnRH-cre+/-;Rosa-CAG-Arch-GFP+/+ OVX mice with bilateral rPOA laser illumination at 593 nm (O, n = 7) or 473 nm (P, n = 6).