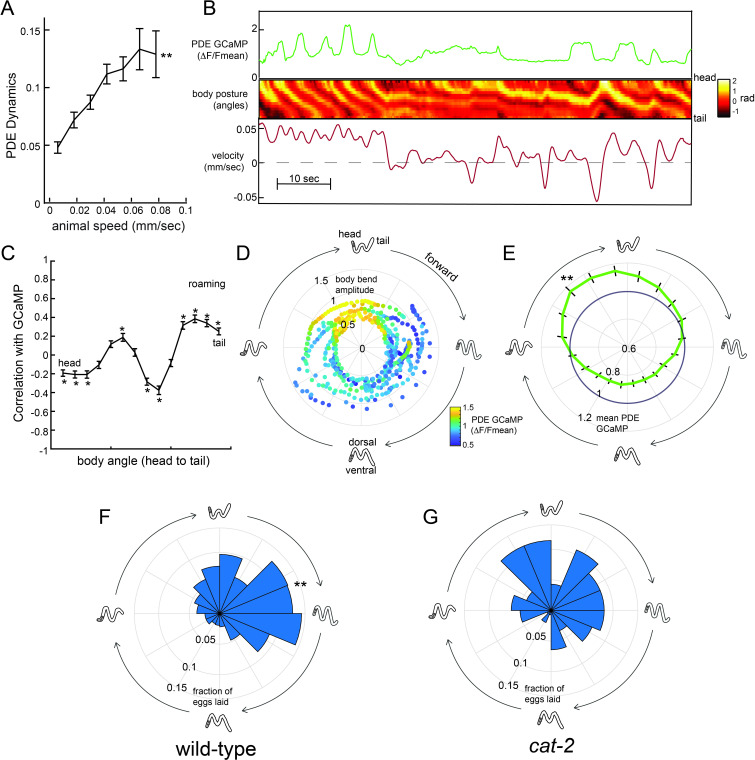
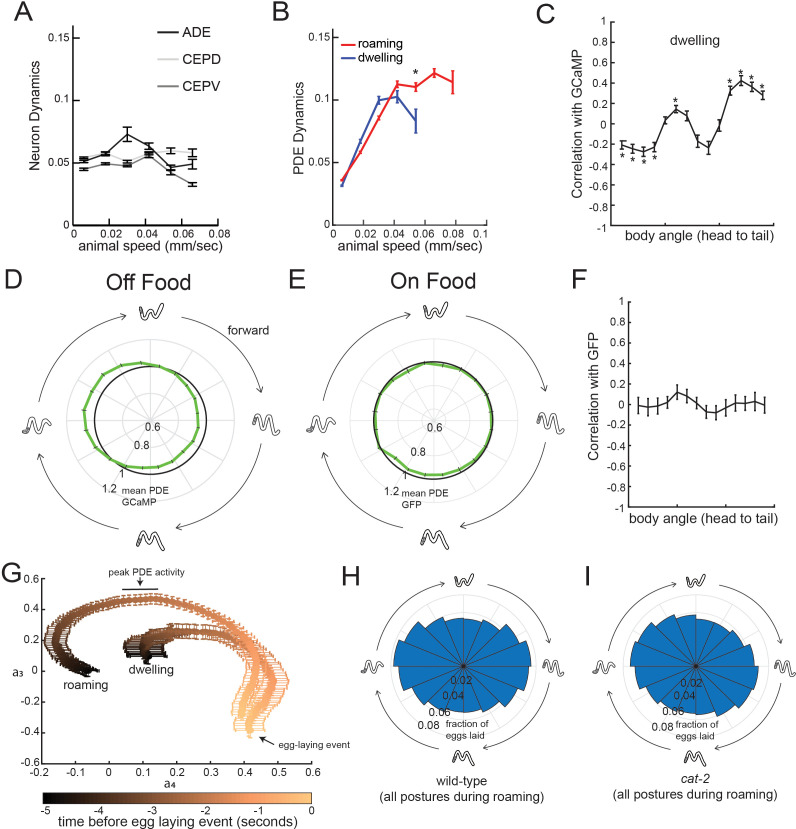
Figure 6. Dopaminergic PDE neurons display activity patterns phase-locked to egg-laying during roaming.
(A) PDE dynamics increase with animal speed. PDE dynamics here is defined as the absolute value of the time derivative of the PDE GCaMP signal. **p<0.001, empirical bootstrap test. (B) Example dataset from a wild-type animal, showing PDE::GCaMP6m signal, body posture (shown as body angles, from head to tail), and animal velocity. (C) Correlation coefficient of PDE activity with each of the 14 body angles. *p<0.05, empirical bootstrap test (Bonferroni-corrected). (D) Example dataset showing how PDE activity (indicated by color) changes as animals proceed through stereotyped forward propagating bends during roaming. Theta values on the polar plot correspond to the phase of the forward propagating bend; radius corresponds to the depth of the body bends (which was quantified as the standard deviation of the mean-subtracted body angles). Corresponding body postures and the direction of the trajectories during forward movement are indicated. Note that PDE activity reliably increases during a specific phase of the forward propagating bend. (E) Average PDE activity at different phases of the forward propagating bend. Theta values are defined as in (D) and the radius indicates the mean PDE GCaMP signal. **p<0.001, Mann-Whitney U test. (F) Histogram depicting frequency of egg-laying events for wild-type animals at different phases during the forward-propagating bend. **p<0.001, Rayleigh z test. (G) Histogram depicting frequency of egg-laying events for cat-2 mutants at different phases during the forward-propagating bend. *p<0.05 versus wild-type, Fisher’s exact test. For (A), (C), and (E), n = 39 animals and data are shown as means ± SEM. For (F) and (G), n = 30 and 10 animals, respectively.