Fig. 4.
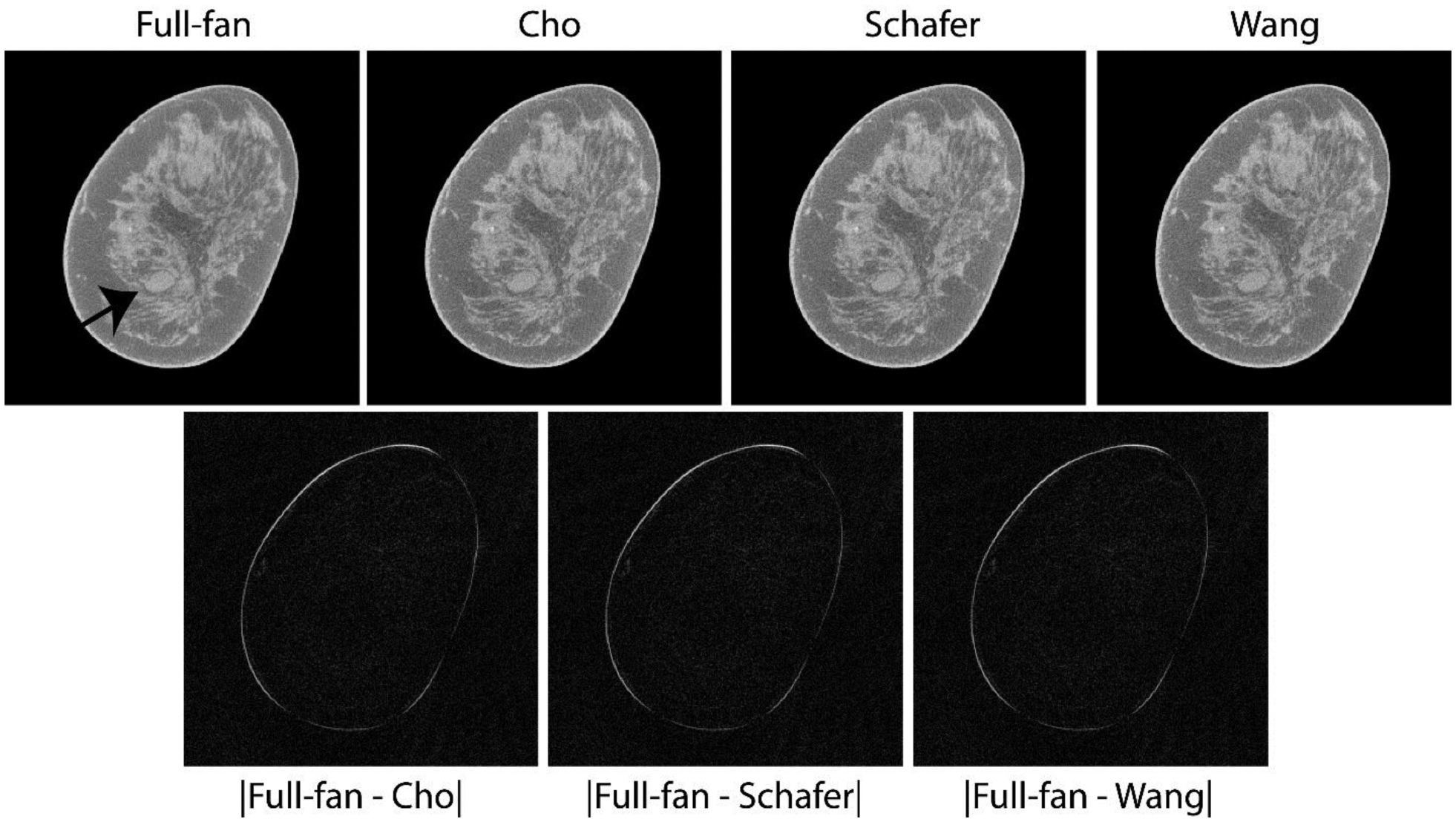
Top row shows matched reconstructed slices with soft tissue abnormality (arrow in top-left panel) that was subsequently pathology-verified to be metastatic adenocarcinoma. The lesion of interest is easily discernible with the truncated-projection (Δθ = 2.72°) CBBCT emulating the laterally-shifted detector geometry and appear visually similar to full-projection CBBCT (top-left panel). Bottom row shows absolute difference between the CBBCT reconstructions of full-projection and truncated-projection datasets with the 3 weighting schemes. The reconstructed linear attenuation coefficients differ predominantly at the skin and appear to be similar across the 3 weighting schemes investigated. Image display scales for the reconstructions (top row) is μ ∈ [0.15,0.35] cm−1 and for the absolute difference images (bottom row) is μ ∈ [0,0.15] cm−1.
