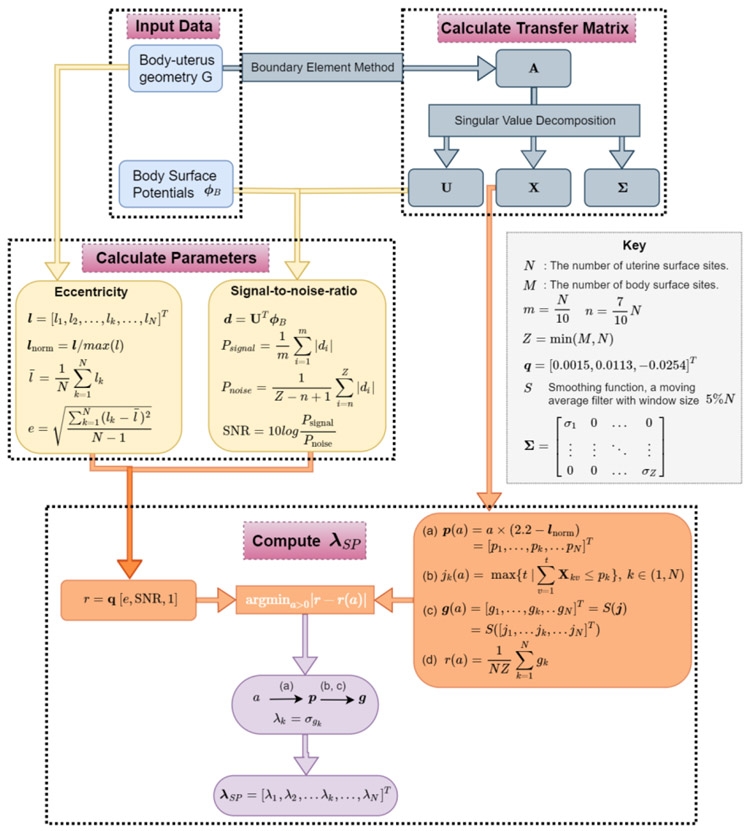
Fig.2. Flowchart of the derivation of λSP.
Body-uterus geometry (G) and body surface potentials (ϕB) are shown in the blue boxes at the top left. Transfer matrix A and its singular value decompositions are shown in the grey boxes at the top right. The eccentricity (e) and signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) are defined and shown in the yellow boxes. M, N, m, n, and Z are defined in the key. The procedure to calculate λSP by minimizing a cost function is shown in the orange boxes. The level threshold function p(a) as a function of unknown variable a is described in equation (a). jk(a) represents the maximum index t of singular basis corresponding to variable a, where in equation (b). g(a) is derived by applying a moving average filter to j, and this process is denoted by S(j) in equation (c). The under-curve ratio r(a) is defined as the ratio between the area under the curve of g(a) and the total area (= NZ) of cumulative X in equation (d). r = q [e, SNR, 1]. By minimizing the difference between r(a) and r, an optimized a can be computed, which can be used compute p, g, λk, and λSP.