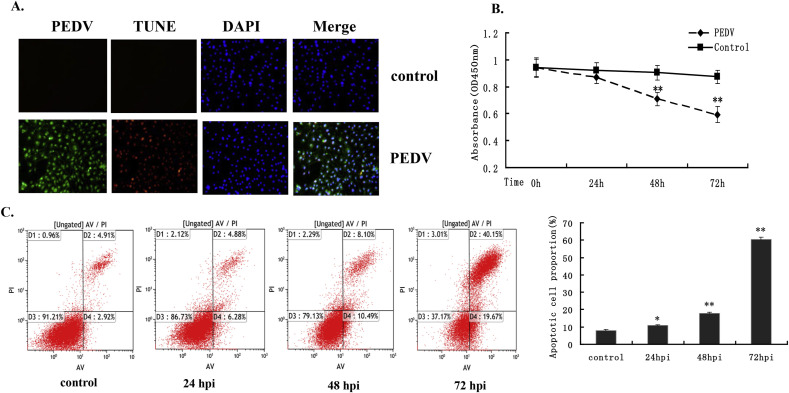
Fig. 3.
Cell apoptosis analysis by CCK8 assay. (A) TUNEL labeling of mock- and PEDV-infected cells. Mock- and PEDV-infected cells were fixed at 48 hpi and subjected to TUNEL assay (red), followed by staining with anti-PEDV-N antibody (green). The cells were then counterstained with DAPI and observed under a confocal microscope at 400× magnification. In merged images, all TUNEL-positive cells were localized within the nuclei of the corresponding PEDV-infected cells. (B) IPEC-J2 cells at 1 × 104 cells/well in 96-well plates were mock-infected of infected with PEDV at an MOI of 1.0. CCK8 assays were performed at various times post-infection. Data presented as absorbance at 450 nm in mock- and PEDV-infected cells at 24, 48, and 72 hpi. Data based on three repeated experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus mock infection. (C) Cell apoptosis analysis by flow cytometry with dual annexinV-PI cell labeling. PEDV-infected cells collected at different time periods were dual-labeled with annexinV and PI and analyzed by FACS. Lower left quadrants represent intact cells (annexinV−/PI−); lower right quadrants represent early apoptotic cells (annexinV+/PI−); upper right quadrants indicate late apoptotic cells (annexinV+/PI−); upper left quadrants indicate necrotic cells (annexinV−/PI+). Figure representative of three independent experiments. Graph on the right represents the percentage of apoptotic cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus mock infection.