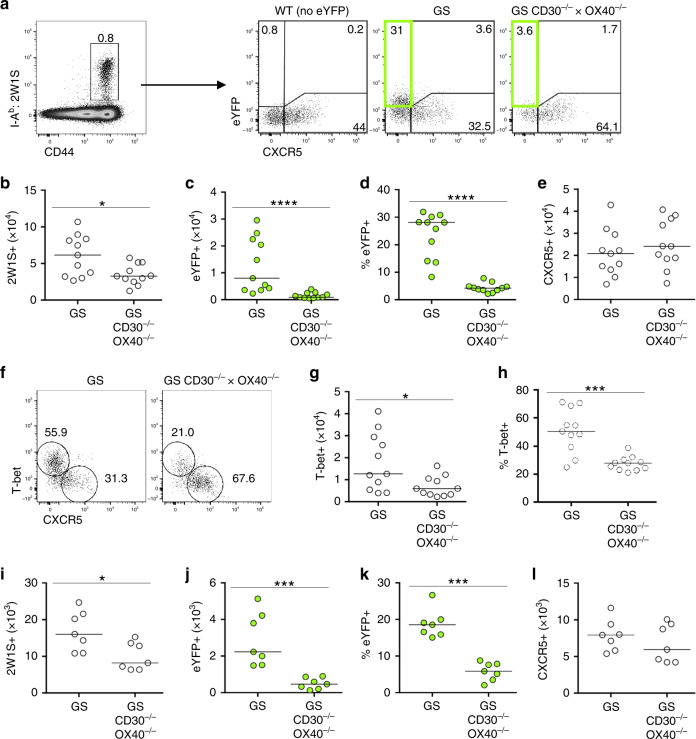
Fig. 1. Mice deficient in CD30 and OX40 show a dramatic decrease in reporting of IFNγ production.
To determine the requirement for CD30 and OX40 on CD4 T cell effector function without ex vivo manipulation, dual IFNγ (eYFP) and IL-17A reporter mice (Great × Smart17A, GS) sufficient or deficient in CD30 and OX40 (GS CD30−/− × OX40−/−) were infected i.v. with Lm-2W1S and the splenic response analysed at 7 (a–h) and 4 (i–l) dpi. a Gating strategy showing identification of 2W1S-specific CD44hi CD4 T cells and their expression of CXCR5 and eYFP in GS and GS CD30−/− × OX40−/− mice. Gated on CD3+CD4+B220−CD11b−CD11c− cells; WT cells (lacking any eYFP) used to establish eYFP gating. Data are representative of 11 mice. b Enumeration of 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells. c Enumeration of eYFP+ 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells. d Percentage of 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells expressing eYFP. e Enumeration of CXCR5+ 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells. f Expression of T-bet versus CXCR5 by 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells. g Enumeration of T-bet+ 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells. h Percentage of 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells expressing T-bet. Data were pooled from 3 independent experiments (n = 11 mice per group). i Enumeration of 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells. j Enumeration of eYFP+ 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells. k Percentage of 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells expressing eYFP. l Enumeration of CXCR5+ 2W1S-specific CD4 T cells. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments (n = 7 mice per group). Values on flow cytometric plots represent percentages; bars on scatter plots represents the median. Statistical significance was tested by using an unpaired, non-parametric, Mann–Whitney two-tailed T test: *p ≤ 0.05, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001.