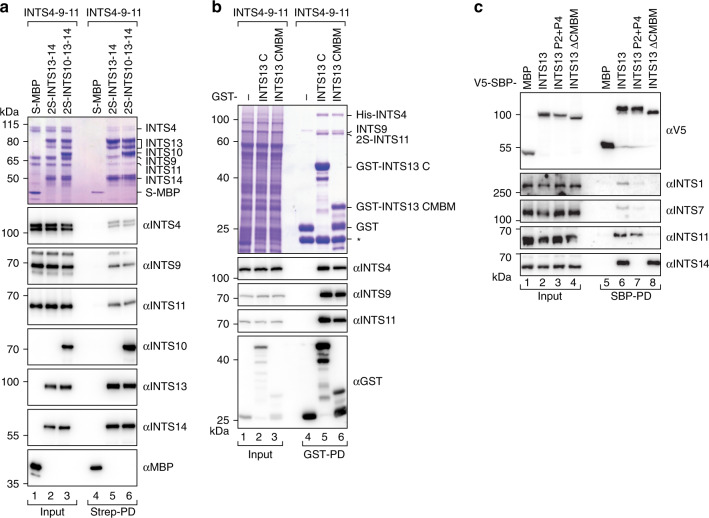
Fig. 5. INTS10–INTS13–INTS14 binds the INT cleavage module via a conserved motif in the INTS13 C-terminus.
a Coomassie-stained gel and corresponding Western blots from copurification of the INT cleavage module (INTS4–INTS9–INT11) with 2S-INTS13–INTS14 or 2S-INTS10–INTS13–INTS14 using purified complexes. S-MBP served as negative control. b Coomassie stained gel and corresponding Western blots from copurification of INT cleavage module from insect cell extracts with GST-INTS13 C-term constructs from E.coli lysates. GST served as negative control. The asterisk marks endogenous GST from insect cells that also binds to GSH-beads. c Coprecipitation of endogenous INT subunits with V5-SBP-INTS13 wild type and mutants. V5-SBP-MBP is included as a control. Inputs (αV5-blot 1%, αINTS14 0.5%, and others 0.1%) and bound fractions (αV5-blot 5%, αINTS14 10%, and others 20%) were analyzed by Western blotting.