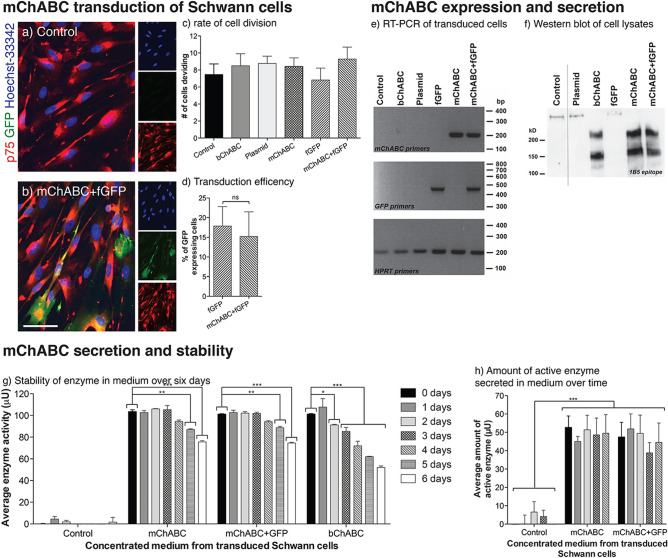
Figure 1.
mChABC can be transduced, expressed, and secreted by Schwann cells. Schwann cells were control, bChABC treated, or transduced with LV-plasmid control, LV-mChABC, LV-fGFP, or LV-mChABC + LV-fGFP (a–d) Images show (a) LV-plasmid control and (b) LV-mChABC + LV-fGFP transduced cells immunostained for Hoechst-33342 (blue); GFP (green) and p75 (red), scale bar = 40 μm. (c) Transduction did not alter rate of Schwann cell division (N = 4, one-way ANOVA F(5,18) = 0.528, p = 0.753). (s) The same transduction efficiencies were achieved for LV-fGFP and LV-mChABC + LV-fGFP cells (N = 30, one-way ANOVA F(5,174) = 6.932, p < 0.0001, post hoc test p = ns). (e–f) mChABC is expressed and secreted by transduced Schwann cells (for full gel see Supplementary Fig. 2). (e) RT-PCR of cells with HPRT, mChABC and GFP primers. (f) Western blot of cell medium probed using anti-1B5 antibody. Dashed line denotes area of cropped image (see Supplementary Fig. 2). DNA and proteins were quantified to ensure equal gel loading. (g–h) Transduced Schwann cells secrete constant amounts of stable mChABC. (g) 100μU of secreted mChABC is more stable at 37 °C than 100μU of bChABC (N = 3, two-way ANOVA: days post transduction F(6,84) = 48.23, p < 0.0001, transduced cell populations F(5,84) = 219.92, p < 0.0001). (h) Amount of active mChABC secreted by transduced Schwann cells over 4 days (N = 3, two-way ANOVA: days post transduction F(6,50) = 0.32, p = 0.8625, cells transduced F(4,50) = 66.01, p < 0.0001).