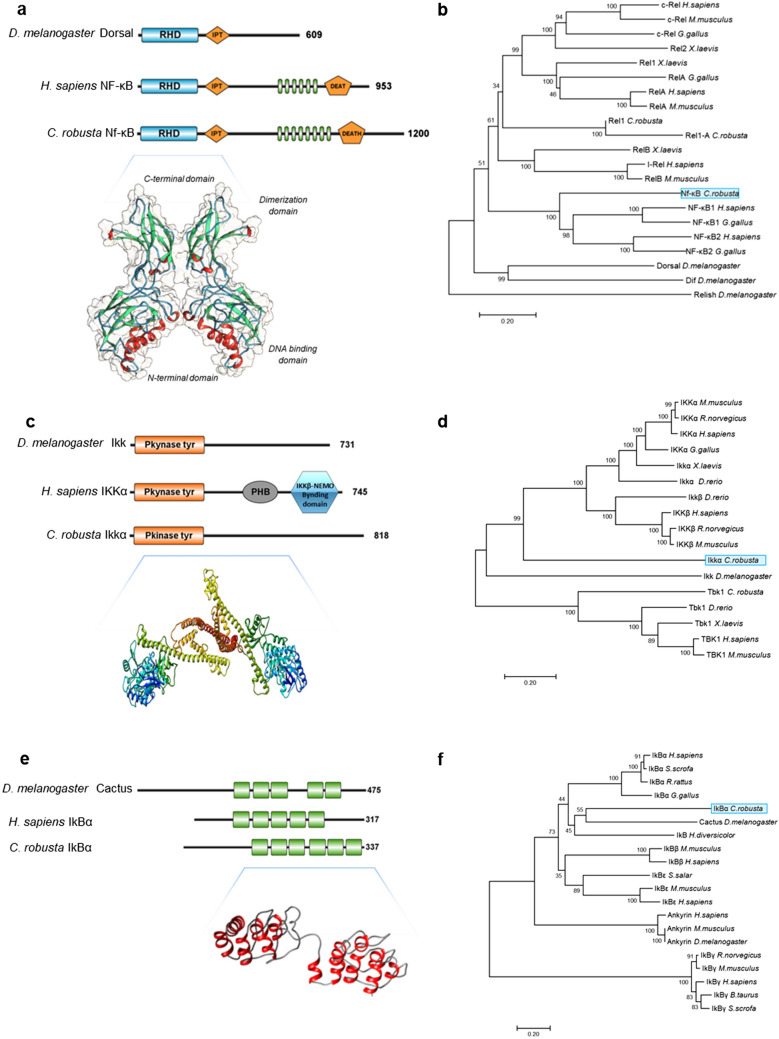
Figure 5.
(a) Comparison of domain organisation in the D. melanogaster Dorsal, H. sapiens NF-κB1 and C. robusta Nf-κB proteins. The RHD domain is in blue, the ANK domain is in green, and the IPT and DEATH domains are in orange. Three-dimensional structures of C. robusta Nf-κB. (b) Phylogenetic tree of NF-κB and Rel family members in vertebrates and invertebrates. (c) Comparison of domain organisation in D. melanogaster Ikk, C. robusta Ikkα and H. sapiens IKKα. The Pkinase-Tyr domain is in orange, the PHB domain is in grey, and the IKKβ/NEMO-binding domain is in blue. Three-dimensional structures of C. robusta Ikkα. (d) Phylogenetic tree of IKK family members in vertebrates and invertebrates. (e) Comparison of domain organisation in the Cactus protein of D. melanogaster, H. sapiens and C. robusta IκBα. The ANK domain is in green. Three-dimensional structures of C. robusta IκBα. (f) Phylogenetic tree of IκB family members in vertebrates and invertebrates. The trees were constructed by the neighbour-joining method and bootstrap analysis. The bootstrap value indicates the number of particular node occurrences per 1,000 trees, as generated by bootstrapping the sequences. The bar indicates the number of amino acid residue substitutions per site. Nf-κB, Ikkα, and IkBα of C. robusta are highlighted in light blue boxes.