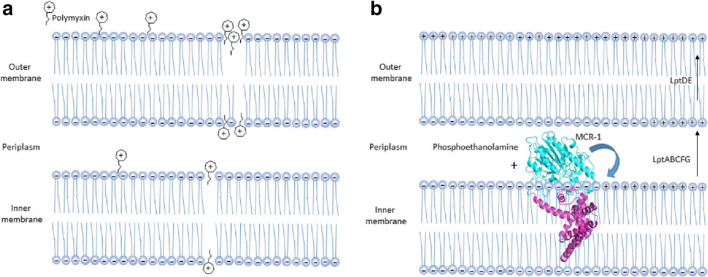
Fig. 2.
Polymyxin activity and working model and mechanism of MCR-1-induced polymyxin resistance. a Polymyxin interacts with the lipid A portion of gram-negative bacteria. The peptides cross the outer membrane and then interact with the cytoplasmic membrane to induce cytoplasmic membrane permeabilization and subsequent cell death. b The integral membrane protein MCR-1 normally localizes to the periplasmic side of the inner membrane and catalyzes the chemical modification of lipid A, yielding PEA-lipid A. The modified PEA-lipid A is then exported by LptABCFG and LptDE into the outer membrane, reducing the negative membrane charge and lowering the affinity of the bacterial surface to the cationic antibiotic polymyxin