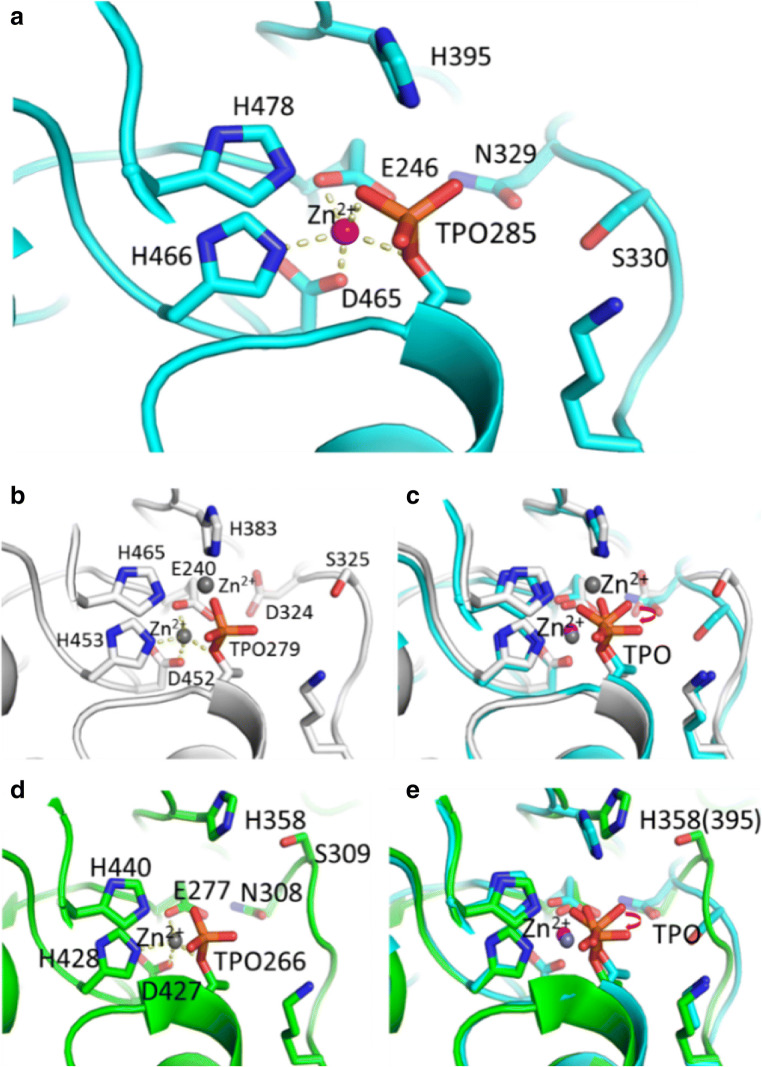
Fig. 4.
High conservation of a catalytic core in cMCR-1, cEptA, and cEptC. a Residues around the Zn2+ ion in cMCR-1. The Zn2+ ion is penta-coordinated, as indicated by yellow dotted lines. Glu246, Asp465, and His466 as well as the hydroxyl oxygen atom of Thr285 and one of the phosphate oxygen atoms are involved in the coordination of Zn2+. b Residues around the Zn2+ ion in cEptA. The coordination of two Zn2+ ions is shown by the yellow dotted line. One oxygen atom in the phosphate group swings aside to coordinate another Zn2+ ion together with H383 and H465. c Superposition of cMCR-1 and cEptA. The oxygen atoms in the phosphate group are shown in different positions by rotating at a specific angle. d Residues around the Zn2+ ion in cEptC. The coordination of Zn2+ is shown by the yellow dotted line. One oxygen atom in the phosphate group swings aside but does not coordinate the Zn2+ ion, unlike in cMCR-1. e Superposition of cMCR-1 and cEptC. The oxygen atoms in the phosphate group are shown in different positions by rotating at a specific angle. Subsequently, the side chain of H358 in cEptC (labeled as H395 in cMCR-1 in the parentheses) swings aside