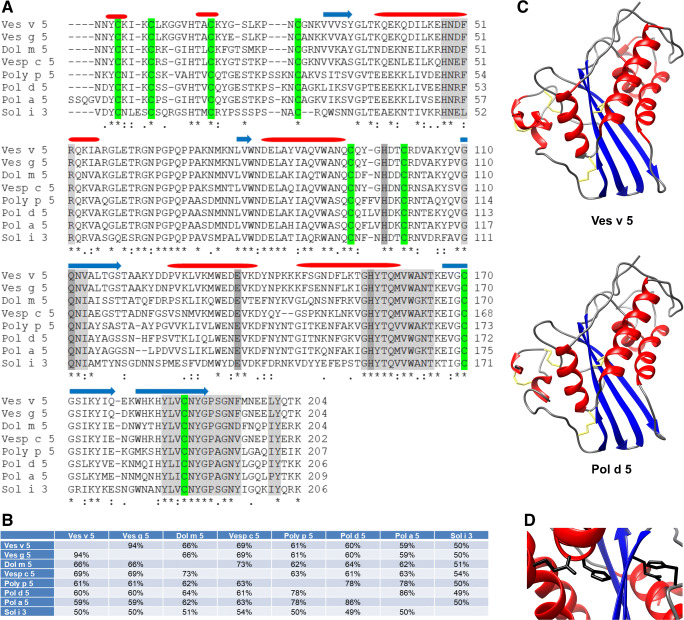
Fig. 1.
Antigen 5 homologues and their structure. a Alignment of the mature sequences of selected Hymenoptera antigen 5 allergens. The secondary structure elements identified in Ves v 5 are indicated above the relevant amino acid sequences (red, α-helix; blue, β-strand). These elements are conserved between the different Ag5 proteins. The CAP signature motifs (CAP3, CAP 4, CAP1, CAP2) and the typical motif [ILVP]Y, which is found near the terminus of Ag5 proteins, are marked in light grey. Conserved residues that form the putative active site are marked in dark grey. Cysteine residues that form disulphide bridges are marked in green. Asterisks, colons and periods indicate identical, conserved and semi-conserved residues, respectively. b Percent identity between the different antigen 5 allergens. Sequence identifiers: Ves v 5 (Q05110.1), Ves g 5 (CAJ28930.1), Dol m 5 (P10736.1), Vesp c 5 (P35781.1), Poly p 5 (P86686.1), Pol d 5 (NP_001310265.1), Pol a 5 (Q05109.1), Sol i 3 (XP_011165202.1). c Crystal structure of Ves v 5 (1QNX) [37] and structural model of Pol d 5 [32••]. α-helices, β-strands and coiled regions are shown in red, blue and grey, respectively. Disulphide bridge-forming cysteines are indicated in yellow. d The solvent-exposed cleft (Ves v 5), which contains the putative active site, formed by a conserved dihistidine motif and conserved residues (Glu, Gln) providing a supporting hydrogen bond network