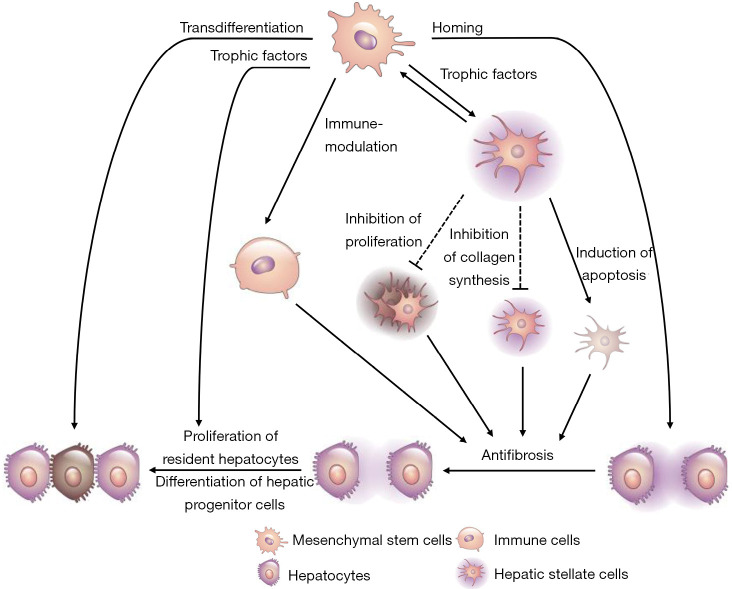
Figure 1.
Potential therapeutic mechanisms of MSCs in hepatic fibrosis. The potential protective mechanisms of MSCs include the following: (I) homing into damaged sites; (II) transdifferentiation into hepatocyte-like cells; (III) suppression of immune reactions; (IV) secretion of trophic factors to suppress the activated hepatic stellate cells and increase the proliferation of both resident hepatocytes and hepatic progenitor cells; and (V) antifibrotic action that results from the regulation of activated hepatic stellate cells and immune cells. The shadows represent the ECM that is secreted from the hepatic stellate cells. Modified from Eom et al. (15). MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; ECM, extracellular matrix.