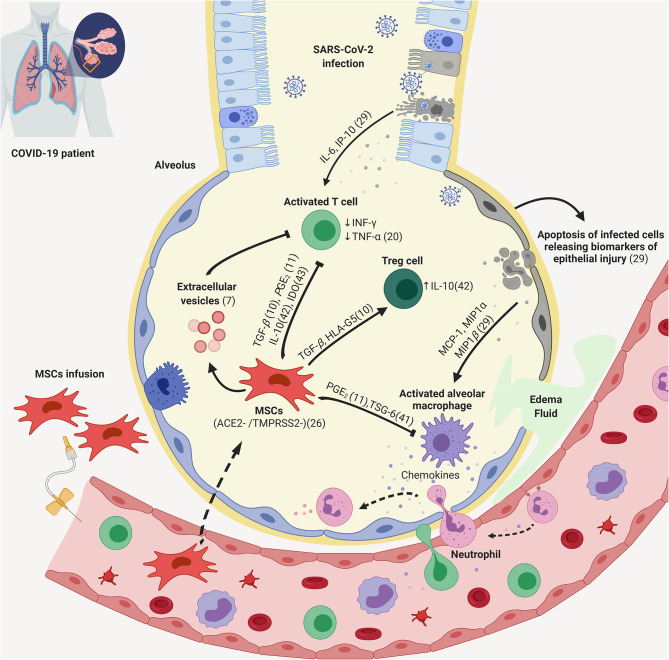
Figure 1.
Putative mechanisms of action of MSCs against lung inflammation caused by COVID-19. During SARS-CoV-2 infection, lung ACE-2 positive cells, such as epithelial and capillary endothelial cells are infected, leading to cell damage, inflammatory signaling, and the release of cytokines and chemokines. The inflammatory milieu promotes the activation of local macrophages, dendritic, and endothelial cells, which further secrete soluble factors and promote the migration of circulating monocytes, granulocytes, as well as lymphocytes. This leads to a feed-forward process, characterized by inflammation, tissue destruction, and organ dysfunction. MSCs and their secretome can be used to counteract inflammation through contact-dependent and also paracrine processes. MSCs, Mesenchymal Stem Cells; Tregs, Regulatory T-cells. Created with BioRender.com.