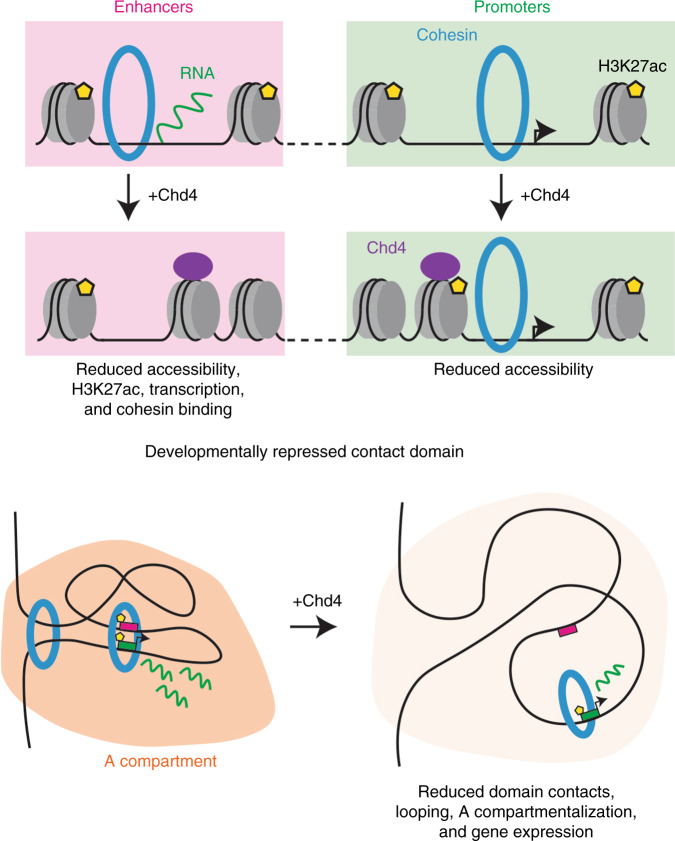
Fig. 6. Chd4 in the control of enhancer function and genome architecture.
(Top) Conditional knockout of Chd4 (purple) in granule neurons of the mouse cerebellum increases the accessibility of gene enhancers (pink) and promoters (mint) genome-wide in vivo. Conditional Chd4 knockout promotes acetylation of histone H3K27 (yellow pentagons), transcription of enhancer RNAs (green lines), and cohesin complex (blue) binding specifically at gene enhancers. (Bottom) Profiling of genome architecture in vivo shows that conditional knockout of Chd4 strengthens domain contacts, looping at loop domain boundaries and between promoters (green) and enhancers (pink), A compartmentalization (orange), and gene expression (green lines) among developmentally repressed contact domains.