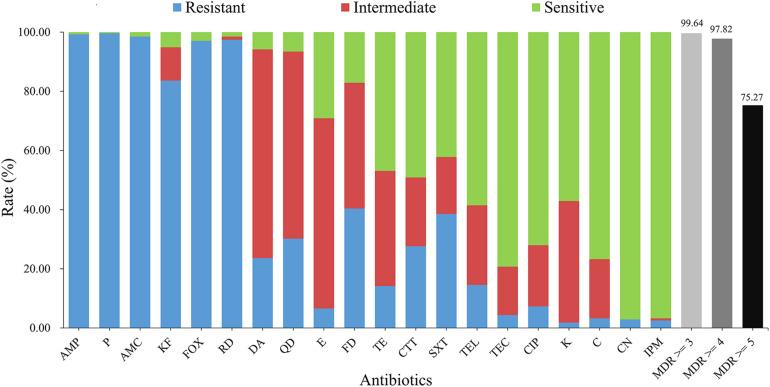
FIGURE 2.
Antimicrobial characteristics of B. cereus from aquatic products. The blue, red, and green bars represent the proportion of resistant, intermediate resistant, and sensitive strains, respectively. The light gray, gray, and black bars show the proportion of strains with multidrug resistance (MDR) to at least three, four, and five classes of antibiotics, respectively. AMP, ampicillin (10 μg); P, penicillin (10 units); AMC, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (20 μg/10 μg); KF, cephalothin (30 μg); FOX, cefoxitin (30 μg); RD, rifampin (5 μg); DA, clindamycin (2 μg); QD, quinupristin-dalfopristin (15 μg); E, erythromycin (15 μg); FD, nitrofurantoin (300 μg); TE, tetracycline (30 μg); CTT, cefotetan (30 μg); SXT, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (1.25 μg/23.75 μg); TEL, telithromycin (15 μg); TEC, teicoplanin (30 μg); CIP, ciprofloxacin (5 μg); K, kanamycin (30 μg); C, chloramphenicol (30 μg); CN, gentamicin (10 μg); IPM, imipenem (10 μg).