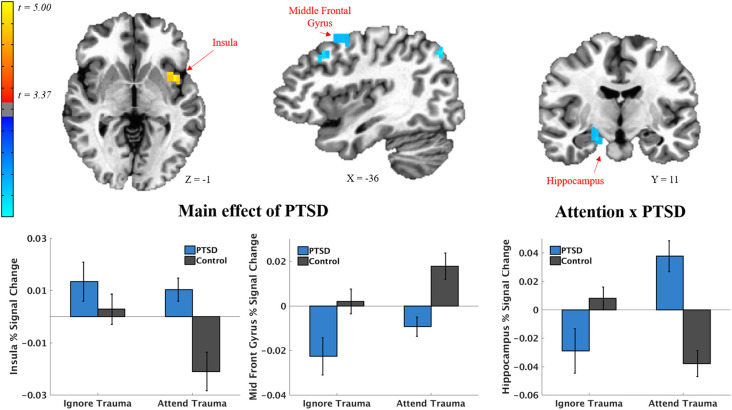
Figure 7.
Significant clusters from group-level LME models of adaptive neurofeedback encoding where there was a main effect of PTSD (left) or interaction (right) with PTSD and attention instruction (attend-to-word vs. ignore word). Adaptive neurofeedback encoding refers to brain region activity that scales linearly with the feedback signal itself. In this paradigm, the feedback signal was the alpha channel (i.e., opacity) of the target stimulus. The feedback signal updated on a trial-by-trial basis depending on the participant’s hyperplane, which itself was determined through the fit of the participant’s brain state on a given trial with the SVM classifier. Higher alpha channels of the target stimulus indicate positive feedback, such that they inherently make the task easier and therefore reinforce brain states that preceded them. Below each significant cluster is a bar graph indicating mean activation differences per task condition as a function of PTSD.